What You Should Know About Wikipedia’s Core Policies

There is no all-seeing Wikipedia judge that oversees “the rules.” But learning those rules takes a lot of effort and is difficult to understand for many people who aren’t fully committed to the Wikipedia community (and I mean really committed). For example, how does Wikipedia decide what’s “neutral,” or if your sources are good enough? And let’s be honest: is anyone really holding contributors to all of these rules—or is it just you who seems to get called out? Is that editor that just sunk your edit out to get you or is she actually following some rule book? Short answer, yes, she is following Wikipedia’s core policies.
One small misstep—citing the wrong source, unintentionally pushing a subjective tone, or unknowingly breaching conflict of interest guidelines—can lead to hours of work evaporating into thin air. And with Wikipedia serving as a top search result for nearly every brand out there, cracking the code on its core policies isn’t just helpful—it’s a huge lever used to build and maintain a strong online reputation.
In this guide, we’ll unpack the foundations that underpin Wikipedia: its core policies, from neutrality to reliable sourcing to conflicts of interest. Whether you’re new to editing or looking to refine your approach, understanding these principles is key to contributing responsibly—and avoiding the frustrations that come with unwitting missteps.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding Wikipedia’s Core Policies and Guidelines
- Understanding Wikipedia’s Core Policies and NPOV Rules
- Wikipedia Core Policies Explained: Avoiding Original Research
- Understanding Wikipedia’s Conflict of Interest Rules
- Why You Don’t Actually Own Your Wikipedia Page
- Why Crypto and Blockchain Struggle on Wikipedia
- Ethical Best Practices for Navigating Wikipedia’s Core Policies
Key Takeaways
The basic rules. At its core, Wikipedia operates on three foundational policies: neutrality, reliable sourcing, and no original research. Think of these as the pillars holding up the “encyclopedia that anyone can edit,” ensuring accuracy and balance no matter who contributes.
Neutrality isn’t about stripping personality; it’s about fairness. The Neutral Point of View (NPOV) principle doesn’t mean your content needs to be robotic—it means presenting all sides of a topic without favoring any. For instance, describing a controversial topic from just one angle is like building a three-legged stool with only two legs: it’s bound to topple over.
Sources are a big deal. Wikipedia tries to rely on verifiable, reliable sources to maintain its credibility. Before adding that glowing blog post or company press release to your page, think critically—does this source hold its own weight in a debate, or will it crumble into dust under scrutiny from the editorial community?
Conflict of interest is a hidden trap many fall into unknowingly. Editing topics you’re closely tied to—whether a company, client, or personal project—isn’t recommended. Imagine trying to referee a game where your team is playing; even with the best intentions, bias can creep in.
You don’t own your company’s Wikipedia page. Many brands are upset about this. Wikipedia entries are a collaboration, owned by the public—not brands, not individuals.
Emerging topics—like crypto—face bigger hurdles on Wikipedia. It’s no accident that newer, contentious subjects struggle to gain traction. Wikipedia editors place extra emphasis on demonstrated reliability and notability.
The real secret to mastering Wikipedia? Play the long game. Editing without understanding the rules is like building a house without checking the blueprints; the building inspector is going to call you out.
Understanding these key principles not only saves you from missteps but positions you as a contributor who adds real value.
Understanding Wikipedia’s Core Policies and Guidelines
Navigating Wikipedia successfully requires a strong grasp of its foundational policies and guidelines, which ensure the platform remains a credible, collaborative, and balanced resource. While Wikipedia is often seen as an open encyclopedia that anyone can edit, this openness comes with necessary rules to foster reliability and fairness. At the base of Wikipedia’s structure lie three core content policies—Neutral Point of View (NPOV), Verifiability, and No Original Research—which dictate how information is created and maintained on the platform.
What Are Wikipedia’s Core Policies?
Wikipedia’s core policies are non-negotiable rules that shape every aspect of content creation and curation. These policies transcend specific topics on the platform and establish clear boundaries for how editors should approach writing, sourcing, and presenting information.
- First, the Neutral Point of View (NPOV) mandates that all content be presented fairly and without bias, prioritizing fact-based reporting over subjective or promotional language.
- Second, Verifiability requires that every claim on Wikipedia be backed by a reliable published source. It isn’t enough for something to be true—contributors must be able to prove it using trustworthy references.
- Lastly, the No Original Research policy draws a line against the inclusion of new ideas, theories, or analysis that hasn’t already been documented in secondary or tertiary sources.
Together, these policies create a framework that tries to ensure Wikipedia entries reflect a well-rounded, evidence-based account of the subject.
Differentiating Policies from Guidelines
Policies answer the “what must you do,” while guidelines guide the “how should you do it.”
- Policies serve as the foundation for Wikipedia’s standards, guidelines offer additional practical advice without the same level of strictness. Policies are binding; failure to follow them very often results in edits being reverted or flagged by the community–especially on highly trafficked pages.
- Guidelines function more like best practices—they provide context, suggestions, and methods for navigating tricky editorial decisions while still falling within the bounds of the core policies. For example, while the NPOV (Neutral Point of View) policy is rigid about neutrality, guidelines such as the “Biographies of Living Persons” document offer detailed advice on handling particularly sensitive subjects.
Understanding the distinction between policies and guidelines not only helps contributors stay compliant but also allows them to approach challenges on Wikipedia with greater finesse.
Why Wikipedia’s Core Policies are so Important
Bottom line: Stick to the policies or your edits will be reverted (reversed).
For contributors, policy adherence means avoiding subjective opinions in articles, relying on reputable sources, and resisting the temptation to inject personal interpretations or unpublished research into content (especially hard for marketers to do). Editors who ignore these rules often find their work undone by others in the community, leading to wasted effort and, in some cases, reputational harm. You also run the risk of another editor adding a template to your page, such as this NPOV dispute template. Once a template is on a page, it can be difficult to remove.
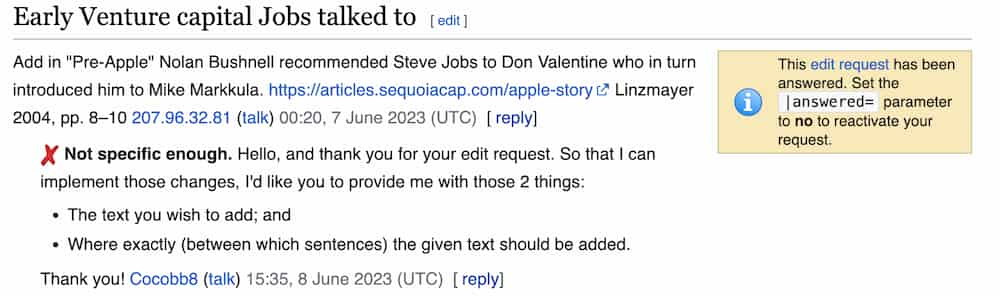
Wikipedia functions on consensus: disagreements are resolved not by a cage fight, but by talking it out (though some editors have far louder voices). Here’s an example of a talk page discussion to edit a Wikipedia page:
Whether you’re updating an article about a niche scientific topic or editing a high-profile political page, respecting and applying these policies makes for productive interactions with others.
Common Misconceptions About Wikipedia’s Rules
Wikipedia’s policies are often misunderstood because they are complex and not engraved in stone, leading to mistakes that can result in content deletions or editor disputes.
One persistent misconception is that including a citation makes any content fair game. The verifiability policy is stricter than that—sources must also meet Wikipedia’s standards of reliability, favoring peer-reviewed journals, established news outlets, and academic publications over personal blogs, press releases, or “fringe” websites.

Another misunderstanding is assuming neutrality means presenting all opinions equally, regardless of their credibility. In reality, NPOV demands a certain proportionality. A fringe theory with minimal support in reputable sources should not receive the same weight as a widely accepted scientific consensus.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Policies
1. Why does Wikipedia prohibit original research?
Original research isn’t allowed because Wikipedia aims to be a tertiary source, summarizing already established knowledge. Allowing novel ideas or unpublished analyses would undermine its reliability and create a platform for subjective interpretations.
2. Can I cite sources like social media or personal blogs?
Generally, that’s a nope. Wikipedia only accepts sources that meet its reliability guidelines. Social media posts, self-published content, and user-generated platforms (like the ascendant Reddit) are rarely considered credible, though there are exceptions for verified accounts of prominent individuals in specific contexts. Sometimes. It’s a gray area.
3. What happens if my edits violate a core policy?
If your content breaches NPOV, Verifiability, or No Original Research, other editors or Wikipedia administrators will probably revert it to an earlier version of the page. Probably the one just before your edit. Repeated violations can lead to warnings, loss of editing privileges, or even bans from Wikipedia.
Understanding Wikipedia’s Core Policies and NPOV Rules
Wikipedia’s foundation as a collaborative, consensus-driven platform rests on a set of core policies designed to ensure the creation of high-quality, impartial, and verifiable content. Among these, the Neutral Point of View (NPOV) principle stands out as a cornerstone, shaping how information is presented and influencing every aspect of content creation on the site. To effectively navigate Wikipedia’s expectations, contributors must thoroughly understand NPOV and its significance.
What is the Neutral Point of View (NPOV) Principle?
The Neutral Point of View requires that all articles on Wikipedia represent information fairly, proportionately, and without editorial bias.
This doesn’t mean that contributors can’t address controversial topics. In fact, Wikipedia encourages such discussions—provided they remain grounded in factual evidence and avoid taking sides. Articles should reflect a balanced overview of the various perspectives on a subject, placing emphasis on viewpoints according to their prominence in reliable sources.
For example, if writing about climate change, it wouldn’t be neutral—or accurate—to give equal weight to the consensus of the scientific community and fringe perspectives that deny climate science. Instead, contributors should ensure the article fairly represents the dominant scientific consensus while briefly acknowledging minority opinions in line with their significance. This careful balancing act ensures the information stays neutral while still addressing differing viewpoints.
How NPOV Impacts Content Creation
NPOV fundamentally shifts how contributors approach writing and structuring content. It’s not sufficient to have an opinion rooted in fact; the author must entirely remove personal judgment from the content. Achieving neutrality requires more than just avoiding subjective language—it means relying on credible sources and adhering to the proportional representation of ideas.
One practical implication of the NPOV principle is the avoidance of “weasel words” or value-laden phrases. For instance, describing someone’s actions as “unjustified” or “heroic” introduces implicit opinions, even when such language feels justified based on the source material. Instead, contributors should stick to verifiable facts and let the sources speak for themselves. Phrases like “critics argue” or “supporters claim” can provide attribution to viewpoints without editorializing.
Another challenge for contributors lies in determining prominence. Wikipedia’s community policies suggest that the importance of a perspective should be directly tied to the weight it receives in reliable, independent coverage. If a topic lacks broad coverage or derives from isolated, niche sources, it may not warrant inclusion in the same depth as more widely-supported ideas.
Examples of NPOV Compliance and Violations
Let’s consider a hypothetical situation involving a Wikipedia article about a recently debated health trend—say, intermittent fasting. A well-written, NPOV-compliant entry would discuss intermittent fasting’s rise in popularity, cite multiple peer-reviewed studies on its benefits, and outline credible critiques from medical professionals. It might also explore social media’s role in promoting the trend, appropriately balancing discussion across reputable sources.
On the other hand, violations of NPOV could take several forms. An article might emphasize unsupported claims about the fasting trend curing diseases, based on anecdotal evidence or unreliable sources, leading to undue weight for fringe theories. Alternatively, the piece could skew too far in criticizing the practice, ignoring credible studies or testimonials that highlight its potential benefits. Either approach erodes neutrality and contradicts Wikipedia’s commitment to unbiased reporting.
In practice, resolving NPOV disputes often requires contributors to revisit the source material, adjust imbalances, and collaborate with other editors to align on the most appropriate presentation of viewpoints. This collaborative review process is essential for ensuring the platform maintains trustworthiness as an open encyclopedia.
By consistently adhering to the NPOV policy, contributors not only uphold Wikipedia’s standards but also enhance their own credibility within the community. The ability to critically evaluate sources and navigate contentious topics with neutrality is a valuable skill that extends well beyond writing for Wikipedia.
Wikipedia Core Policies Explained: Avoiding Original Research
Original research is one of Wikipedia’s biggest red flags, and understanding this policy is essential for anyone contributing to the platform. At its core, the “no original research” rule ensures that Wikipedia remains a reliable, verifiable repository of knowledge rather than a place for new theories, personal opinions, or unique interpretations.
Understanding the “No Original Research” Rule
Simply put, Wikipedia prohibits contributors from adding content that hasn’t already appeared in a reputable, published source. This means you can’t use Wikipedia to debut your own ideas, combine information from different sources to develop new conclusions, or reinterpret data to provide novel insights. The platform exists to summarize what’s already out there, not to create content that advances new arguments or perspectives.
For example, it might be tempting to analyze statistical data from different government reports and draw an original conclusion about a trend. However, if those conclusions haven’t been explicitly made in a published, reliable source, they would violate Wikipedia’s policy. Even seemingly small editorial additions—such as adding commentary or making speculative connections between facts—can unintentionally cross the line into original research territory.
Analyzing Sources: What Qualifies as Reliable?
The policy against original research goes hand-in-hand with Wikipedia’s emphasis on verifiability through reliable sources. Reliable sources are defined as published materials with a proven track record of accuracy, credibility, and editorial oversight. Peer-reviewed academic journals, reputable news outlets, and books from authoritative publishers are generally considered safe bets.
On the other hand, personal blogs, self-published works, and unvetted online content usually don’t meet Wikipedia’s reliability standards, as they lack the necessary scrutiny to ensure accuracy. For instance, citing a blog post to support a claim about a major scientific discovery isn’t just a reliability issue—it also opens the door to original research if the blog discusses ideas or interpretations not grounded in verifiable data.
When evaluating sources, prioritize those that directly address your topic and avoid cherry-picking evidence to fit your narrative. A good practice is to look for multiple, independent references to support a single statement, especially for contentious or nuanced subjects.
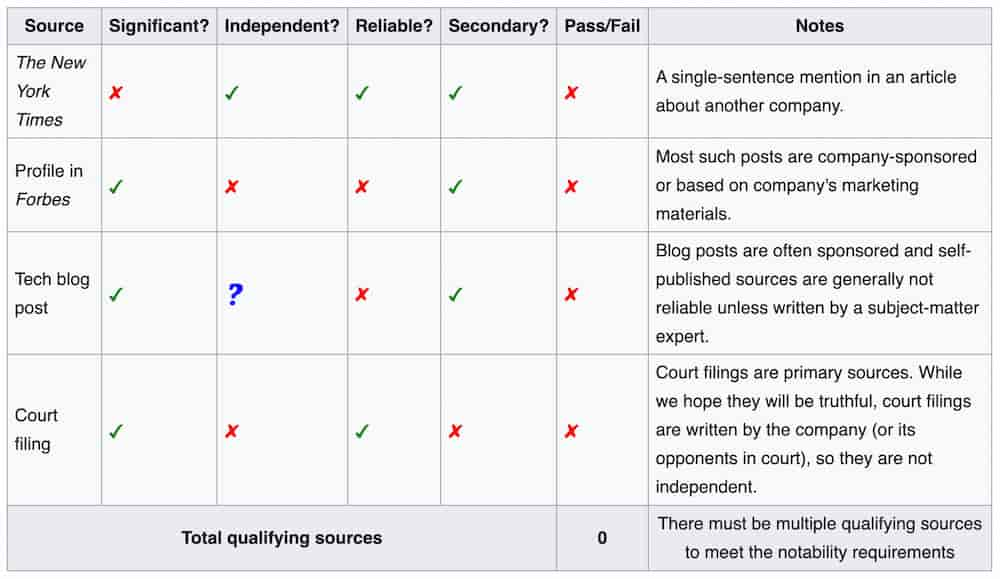
How to Avoid Original Research in Your Contributions
Staying on the right side of this policy requires an intentional approach to sourcing and writing. First, ensure that every claim or piece of information you add can be directly linked to a specific, trusted source. When paraphrasing, stick closely to the source material’s intent and avoid introducing interpretative flourishes—this is where original research often creeps in.
Second, resist the temptation to synthesize new ideas from multiple sources. For instance, if two separate studies suggest indirect connections between two factors, it’s not permissible to add a sentence combining those studies to claim a definitive causal relationship unless a published source explicitly states it. If you do this, it puts you at risk of violating Wikipedia’s no original research policy.

Finally, when in doubt, consult Wikipedia’s discussion pages or seek input from experienced editors. If a contribution feels innovative or groundbreaking, it’s best to step back and evaluate whether it aligns with Wikipedia’s role as a tertiary source. Originality may be a virtue in some contexts, but on Wikipedia, sticking to what’s documented and verifiable is the key to building trust and maintaining credibility.
By rigorously avoiding original research, contributors help uphold Wikipedia’s integrity and ensure that it remains a reflection of widely accepted knowledge—not a platform for speculation or individual interpretation. This principle, while sometimes challenging to navigate, is foundational to Wikipedia’s goal of being a reliable, unbiased resource for users worldwide.
Understanding Wikipedia’s Conflict of Interest Rules
Wikipedia thrives on the principle of neutrality, ensuring its content reflects unbiased, fact-based information. The platform’s Conflict of Interest (COI) rules are designed to protect this neutrality by addressing situations where personal, professional, or financial connections may compromise the integrity of contributions. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is essential for anyone who contributes to Wikipedia—whether as a casual editor or a representative of an organization.
Defining Conflicts of Interest on Wikipedia
A conflict of interest arises when someone’s connection to a subject might cloud their judgment or affect their ability to contribute neutrally. On Wikipedia, this typically means editing topics where you—or the organization you represent—have a direct stake. For example, editing a page about your company, employer, or a competitor can introduce bias, even if the edits are unintentional. Personal relationships, investments, or promotional motives can also create conflicts, raising questions about whether edits are being made with impartiality or self-interest.
Wikipedia doesn’t outright ban COI editing but strongly discourages it. Editors with potential conflicts are expected to exercise caution by following the platform’s disclosure guidelines, using neutral language, and working through proper editorial channels rather than directly making changes to relevant articles.
It’s always best to disclose any COI outright when using Wikipedia.

Identifying and Disclosing Potential Conflicts
The first step to handling COI issues is recognizing when they apply to you. If you’re deeply connected to a subject—whether it’s through employment, affiliation, or personal interest—you should assume that your edits might be viewed as a conflict. Wikipedia encourages transparency in these cases. You can disclose a potential conflict of interest on your user page or talk pages related to the subject matter, allowing the broader community to evaluate your contributions in context.
It’s also wise to avoid editing directly when a COI exists. Instead, editors are encouraged to suggest changes on the talk page of an article rather than editing the article itself. This process allows impartial editors to evaluate and implement appropriate updates, ensuring that content complies with Wikipedia’s core policies.
Strategies for Adhering to Conflict of Interest Guidelines
Maintaining ethical integrity while navigating COI rules requires careful planning and restraint. Here are a few strategies to stay compliant:
Engage in talk page discussions: Rather than taking matters into your own hands, use article talk pages to propose edits, providing sources to back up your suggestions. This collaborative approach allows other editors to review contributions from an unbiased perspective.
Stick to third-party, reliable sources: Content must be verifiable and based on independent, reliable sources. Avoid using press releases, company websites, or self-published materials, as these are often considered biased.
Avoid promotional language: Even unintentional marketing or self-serving phrasing can raise red flags. Aim for factual, evidence-based contributions that reflect the balanced tone Wikipedia strives to uphold
Consult Wikipedia guidelines: If you’re unsure about where to draw the line, resources like Wikipedia’s COI guideline and the “plain and simple conflict of interest guide” provide practical advice for ethical behavior.
By balancing cautious self-awareness with an openness to collaborative processes, contributors can respect Wikipedia’s mission for neutrality while still participating meaningfully in the platform’s knowledge ecosystem.
Why You Don’t Actually Own Your Wikipedia Page
Addressing the Ownership Myth
It’s a common misunderstanding: people assume that because a Wikipedia page is about them or their business, they somehow “own” it. After all, the subject seems personal—your name, your company’s story, your legacy.
Wikipedia is not designed to grant ownership to its subjects. Instead, the platform operates as a collaboratively edited encyclopedic resource where content is governed by community standards rather than individual interests.
The ownership myth likely arises because Wikipedia pages are highly visible and often rank prominently in search engine results. It’s natural to feel a personal connection or even a sense of authority over the content you believe represents you. However, Wikipedia explicitly states that no one—not even the subject of the article—owns a page. This fundamental principle ensures that content remains impartial, free from promotional bias, and adheres to the community-driven ethos at the core of Wikipedia’s mission.
Who Controls a Wikipedia Page?
If not you, then who? The answer isn’t a single person or entity—it’s the community of contributors and administrators who collectively maintain and update the platform. Wikipedia uses an open editing model, meaning anyone can edit almost any page (as long as the changes comply with Wikipedia’s guidelines and policies). Moderators and experienced editors serve as watchdogs, stepping in to resolve disputes, enforce standards, or undo edits that violate core principles like neutrality or verifiability.
What’s unique about this system is that the “control” of a page is decentralized. Any valid contribution, whether it’s from a seasoned editor or a brand-new user, is subject to scrutiny and may be challenged if it doesn’t align with Wikipedia’s policies. Even administrators—those with additional technical privileges—can’t dictate content based on their preferences. Their role is to enforce rules, not to hold creative control.
This lack of individual ownership can feel frustrating, particularly when edits to your page portray your work or business in a way you feel is incomplete or unflattering. Yet, it’s precisely this community-centered model that keeps Wikipedia from becoming a platform for self-promotion or unchecked bias.
Contributor Rights and Limitations
As someone connected to the subject of a page, you’re not entirely excluded from the editing process, but your rights as a contributor are more limited than you might expect. Wikipedia’s conflict of interest (COI) guidelines discourage subjects from directly editing articles about themselves. Why? Because even well-intentioned contributions from involved parties are often colored by their own perspectives, making neutrality—a cornerstone of Wikipedia’s content policies—hard to maintain.
If you believe that critical information is missing from your page, the recommended course of action is to propose edits on the article’s talk page, a public forum attached to every Wikipedia article where discussions about content take place. This allows the broader editing community to evaluate your suggestions in light of Wikipedia’s guidelines. Keep in mind, though, that reliable third-party sources are required to substantiate any claims or additions. Personal anecdotes or unpublished data won’t meet the site’s rigorous standards for verifiability.
Even more importantly, while you may feel invested in how the page represents you, attempting to exert control through persistent direct edits or overly promotional content is almost certain to backfire. Editors are well-trained to spot COI behavior and will likely revert such changes—or worse, flag the article for potential removal.
This unique system of distributed oversight is what makes Wikipedia truly distinct. It creates a level playing field where no single individual’s agenda can override the shared principles of transparency, accuracy, and neutrality. Understanding this balance can help you navigate your involvement with your Wikipedia page more effectively while respecting the community’s mission to serve as an unbiased informational resource.
Why Crypto and Blockchain Struggle on Wikipedia
Analyzing Wikipedia’s Stance on Emerging Technologies
Wikipedia fundamentally operates as a community-driven encyclopedia, governed by strict policies designed to ensure neutrality, reliability, and verifiability. Emerging technologies like cryptocurrency and blockchain often push against these boundaries, making it particularly challenging for their advocates to achieve robust, unbiased coverage on the platform. The underlying issue stems from the disparity between the fast-evolving, decentralized nature of these technologies and Wikipedia’s deliberate reliance on well-vetted, secondary sources that reflect established consensus in the wider world.
Blockchain and cryptocurrency topics are often burdened by polarized perspectives, with their advocates championing them as revolutionary tools for financial independence and decentralization, while detractors see them as overhyped, sometimes exploitative mechanisms with unclear long-term implications. This ideological tension can create hurdles for contributors attempting to maintain Wikipedia’s “Neutral Point of View” (NPOV) principle. Even when editors aim to present balanced narratives, the existing body of reliable sources tends to sway toward either advocacy or skepticism, leaving little room for truly neutral, comprehensive coverage. Wikipedia’s editors act as gatekeepers, and when content is perceived as promotional or speculative—frequent criticisms levied at crypto-related articles—topics are flagged, heavily revised, or outright rejected.
Challenges Faced by Crypto and Blockchain Topics
A primary obstacle for cryptocurrency and blockchain coverage on Wikipedia is the platform’s strict sourcing requirements. Wikipedia values information derived from credible, secondary sources such as academic journals or reputable news outlets. Unfortunately, extensive academic analysis of these technologies often lags behind their rapid development cycles, leaving much of the dialogue to be shaped by sources that Wikipedia’s editors deem questionable—startup blogs, niche crypto publications, or opinion pieces. For example, an editor writing about a new blockchain platform may struggle to find coverage in mainstream outlets, even if the platform has demonstrated significant technological advances.
Additionally, the sheer prevalence of marketing and hype surrounding cryptocurrencies poses another challenge. Many crypto projects treat Wikipedia as just another social media platform to amplify their brand, flooding article drafts with promotional language and unverifiable claims. This behavior triggers Wikipedia’s community of editors to adopt a more skeptical, defensive posture toward all crypto-related content, even when well-intentioned contributors attempt to create factual, policy-compliant entries.
Furthermore, blockchain as a concept often intersects with complex technological or financial systems that require specialized knowledge to explain and contextualize effectively. Wikipedia’s editor base includes volunteers with varying expertise levels, and when complex topics fail to attract editors proficient in the subject matter, misinformation or overly simplistic narratives can dominate. This issue is compounded by the technical jargon and niche terminology inherent to blockchain technology, which can alienate both casual readers and general-purpose editors alike.
Tips for Improving Coverage in Contentious Areas
Successfully navigating Wikipedia’s core policies to improve blockchain and crypto topic coverage requires a thoughtful, policy-aligned approach. Contributors should start by locating thoroughly vetted, mainstream sources to establish a strong foundation of reliable references. Publications such as The New York Times, The Financial Times, or peer-reviewed journals lend credibility to content and minimize objections during the editing process. When mainstream coverage is sparse, contributors can still use industry-specific reports and expert analyses, provided these sources meet Wikipedia’s guidelines for reliability.
Beyond sourcing, contributors need to craft their narratives with scrupulous neutrality. Avoid using promotional language, even when describing legitimate achievements, as Wikipedia frowns on content that appears to advocate for or against a topic. Instead, focus on presenting a balanced overview of the subject, addressing both its potential benefits and criticisms through cited examples.
Engaging with Wikipedia’s editorial community can also dramatically improve outcomes. Proactively joining discussions on Talk pages, addressing flagged concerns promptly, and seeking feedback from experienced Wikipedia editors fosters collaboration and helps avoid conflicts that could derail an article. In contentious areas like cryptocurrency, such collaborations are particularly valuable to ensure entries comply with Wikipedia’s Neutral Point of View (NPOV) and verifiability standards.
Navigating Wikipedia’s policies can be frustrating for those passionate about blockchain and crypto, but adherence to its core principles—consistency, neutrality, and factual rigor—can significantly improve outcomes.
By respecting Wikipedia’s policies and building meticulously sourced, unbiased content, contributors can help ensure a more accurate and comprehensive representation of these emerging technologies on the platform.
Ethical Best Practices for Navigating Wikipedia’s Core Policies
Navigating Wikipedia’s policies can feel like walking a tightrope, especially if you’re contributing on behalf of a company, brand, or public figure. The encyclopedia’s policies are deeply rooted in principles like neutrality, verifiability, and ethical conduct, and any misstep—whether intentional or accidental—can erode trust within the community or, worse, lead to issues like removal of content or editing privileges. To safeguard your reputation and contribute meaningfully, it’s essential to not only follow the rules but also adopt ethical practices that go beyond the bare minimum.
Collaborating Responsibly Within Wikipedia’s Framework
At its core, Wikipedia is a collaborative environment powered by a volunteer community. Respecting this collaborative nature means prioritizing transparency and good-faith interactions. If you represent an organization or have a vested interest in a topic, identify yourself honestly on your user page. Not only is this required by Wikipedia’s conflict of interest (COI) guidelines, but it also establishes credibility and trust with other editors.
When proposing edits to articles, use the article’s talk page to share your suggestions rather than editing it directly. For example, instead of attempting to rewrite a section yourself, describe the changes you’d like to see and include justification that cites reliable, third-party sources. This demonstrates respect for the existing editorial process and allows neutral editors to make an unbiased evaluation. Remember, Wikipedia thrives on consensus, so engaging constructively—even when disagreements arise—is imperative.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Navigating Wikipedia ethically also means steering clear of tactics that may seem harmless but can jeopardize your standing. One common mistake is cherry-picking sources or selectively quoting evidence to paint a narrative favorable to your interests. Even if unintended, these actions can violate Wikipedia’s Neutral Point of View (NPOV) policy, which requires all contributions to be balanced and unbiased.
Similarly, avoid creating or editing articles about your organization, employer, or affiliates directly. This is a clear red flag for the community and can lead to accusations of bias or, worse, outright removal of your edits. Instead, work through proper disclosure channels and suggest edits thoughtfully, presenting facts backed by reliable sources rather than marketing language or subjective claims.
Another frequent pitfall is relying on low-quality sources to support your contributions. Wikipedia values verifiability and credibility, meaning citations should come from established, independent publications rather than blogs, press releases, or self-published content. If you’re unsure whether a source is appropriate, it’s worth checking Wikipedia’s guidelines on reliable sources or consulting with experienced editors on the talk page before proceeding.
Maintaining Transparency While Contributing
True transparency starts with accountability. Declaring conflicts of interest is just one aspect; it’s equally important to ensure that all your edits and suggestions are data-driven and meet Wikipedia’s standards for accuracy. When recommending changes, always provide detailed edit summaries or talk page explanations. These notes not only help other editors understand your rationale but also demonstrate your commitment to ethical collaboration.
Proactive engagement can also elevate trust. For instance, if a dispute arises, defer to community moderators or established editors rather than doubling down defensively. Approaching such situations with humility shows that your priority is improving the information rather than advancing personal or corporate agendas.
Another way to stay transparent is to focus on content areas unrelated to topics where you might have a conflict of interest. By building respect as a contributor on broader topics, you foster goodwill and establish a reputation as someone aligned with Wikipedia’s shared mission of knowledge dissemination.
Ultimately, navigating Wikipedia’s policies ethically is less about rigidly ticking off a checklist and more about embodying the values that underpin the platform. Ethical contributions require diligence, transparency, and respect for the process—qualities that not only ensure compliance but also build long-term credibility within the community.
Conclusion
Wikipedia isn’t just a reflection of what the world knows—it’s a mirror of how the world sees your brand. For marketers and brand managers, this realization underscores a powerful truth: reputation isn’t confined to press releases or social media campaigns. It’s shaped, debated, and sometimes challenged in public, collaborative spaces like Wikipedia, where neutrality and verifiability set the standard. Embracing this process doesn’t just elevate your knowledge of the platform—it also strengthens your role as a steward of credibility.
Think of engaging with Wikipedia not as an obligation but as an opportunity to contribute to the broader conversation about your industry or organization. By adhering to principles like neutrality and transparency, you can align not just with Wikipedia’s policies but with a higher standard of online integrity—demonstrating to both stakeholders and an ever-watchful internet audience that your brand values truth over spin. The challenge is clear: Are you ready to cement your digital legacy with substance, not shortcuts?
