How Wikipedia Handles Deletion: Speedy, Proposed, and AfD

Wikipedia articles don’t disappear randomly—Wikipedia employs several structured processes to determine which content stays and which has to go. Some removals occur swiftly, others offer a grace period, while some become full-blown community deliberations that could go either way. The Wikipedia deletion process is not always straightforward, so it is worth reviewing the different deletion pathways you may encounter.
Understanding these deletion systems matters, especially if managing your organization’s online reputation is part of your role. Knowing ahead of time what might trigger a rapid deletion or a more deliberative process can help you proactively manage your content and avoid unexpected removals.
TL;DR
Three distinct processes for different situations: Speedy deletion acts quickly, with minimal debate—ideal for clear violations. Proposed Deletion (PROD) provides a seven-day window to resolve issues. Articles for Deletion (AfD) engages the community in a structured, open discussion.
Timeframes matter—response speed makes the difference: Speedy deletion moves fast, leaving little room to contest or edit. PROD provides a meaningful window to strengthen content. AfD offers ongoing opportunities to advocate for the article, but can extend uncertainty during discussions.
Level of community engagement varies a lot: Speedy deletion largely excludes community input (it’s a nuke). PROD leverages limited collaboration. AfD conversations involve extensive community participation, shaping consensus-based outcomes.
Opportunity to make improvements differs: Speedy deletion offers almost no opportunity to revise flagged content. PROD and AfD are designed to allow proactive improvements that can potentially save an article.
Integrity and quality drive Wikipedia’s decisions: All deletion methods focus on maintaining Wikipedia’s content standards. Aligning articles proactively with these guidelines reduces risk and builds trust among editors.
Key Differences Between Speedy, PROD, and AfD
Wikipedia employs three distinctly different processes—Speedy Deletion, Proposed Deletion (PROD), and Articles for Deletion (AfD). Each approach serves a specific purpose and responds to different scenarios. Understanding these differences can help you address deletion risks more strategically and effectively.
| Deletion Type | Speed | Who Can Tag It | Defense Opportunity | Common Reasons | Recovery Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speedy Deletion (CSD) | Immediate (Minutes) | Any editor | Minimal to none | Spam, no context, blatant promo | Userfy or appeal to admin |
| Proposed Deletion (PROD) | 7 days | One editor | Can contest within 7 days | Weak notability, lack of sourcing | Remove tag + explain on Talk page |
| Articles for Deletion (AfD) | 7+ days | Any user, community votes | Full community discussion | Controversial, not notable | Argue in AfD page or recreate with better sourcing |
Timeframes and Urgency
Think of Speedy Deletion as the express lane for obvious violations—articles disappear quickly, often within hours or even minutes. For example, if an entry about a startup feels blatantly promotional (“We’re the best, and everyone loves us!”), an admin might remove it immediately and without debate.
PROD, on the other hand, gives contributors about seven days to make necessary improvements, such as adding better references or neutralizing tone. If someone contests it during that window, the deletion is halted, and discussions may ensue.
The AfD is the slowest and most deliberative process. Community members discuss an article thoroughly for about a week. Here’s where advocates can present solid evidence of coverage or demonstrate notability. While stressful at times, it allows teams managing brand reputation to carefully build their case step by step.
Involvement of Community
Speedy Deletion decisions are typically made by a single administrator, based solely on predefined criteria. There is virtually no community input, and the content owner may not even realize there is a problem until it’s too late.
PROD slightly increases community involvement because the seven-day period encourages other editors to either improve an article or contest the deletion. It’s less adversarial than AfD and more collaborative when done right.
AfD is a fully community-driven process. Discussions take place openly with multiple editors providing recommendations backed by Wikipedia policy. For instance, if there is contention over whether a prominent local business merits inclusion, various editors debate its coverage and cite relevant guidelines. The process is more rigorous but also more transparent.
Opportunity for Improvement
Of these methods, Speedy Deletion provides almost no opportunity to remedy flagged issues. Once content is tagged, removal is usually immediate unless contested urgently.
Both PROD and AfD explicitly welcome improvements during the decision period. With PROD, organizations have 7 days to significantly upgrade articles—adding legitimate references, tightening language, and clearly demonstrating notability. AfD offers even more flexibility, as edits introduced during the debate can directly influence the community’s voting. If your organization’s profile initially lacks robust references but incorporates reputable independent sources during the AfD, editors may shift towards retention.
Understanding these nuances helps you craft a proactive Wikipedia strategy, turning potential deletion threats into opportunities for reinforcing your organization’s credibility.
Speedy Deletion: Quick and Immediate
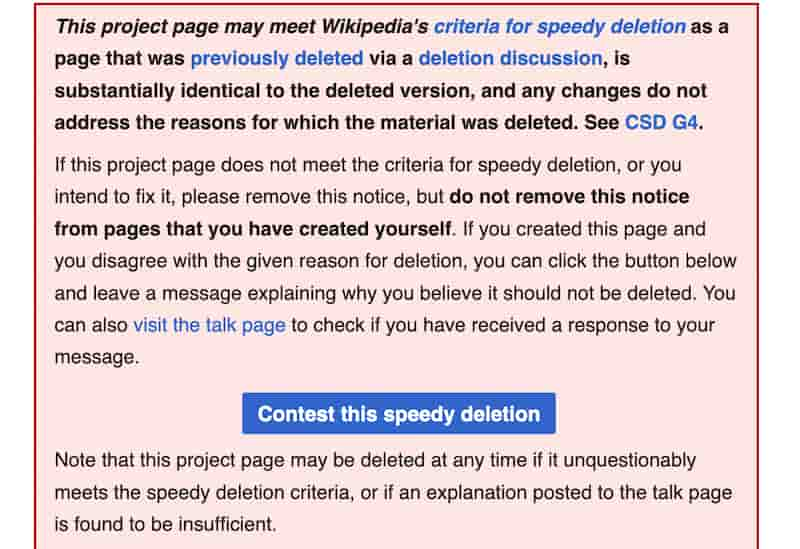
Wikipedia reserves Speedy Deletion for clearly problematic content that requires minimal discussion before removal—articles considered obvious policy violations.
Criteria for Speedy Deletion
The qualifying issues are straightforward:
- Blatant self-promotion (“Greatest company ever!”)
- Gibberish and nonsense
- Empty placeholders
- Identical copies of existing pages
An admin quickly evaluates against strict criteria, then quickly starts the Wikipedia deletion process without engaging the broader community.
Here’s an example—a company’s entirely promotional new page proudly announcing they’re “the ultimate in customer satisfaction!” with few or no sources. It fits the “blatant advertising” criteria perfectly, and swift deletion happens almost instantly.
Advantages of Speedy Deletion
From Wikipedia’s perspective, speedy deletion maintains quality by swiftly removing inappropriate content without drawn-out arguments that clog the site. For organizations, speedy deletion can serve as rapid protection against harmful pages, such as maliciously posted defamatory content.
But it also underscores the importance of proactively aligning your content with Wikipedia guidelines upfront—speedy deletion leaves no leeway for corrections after flagging.
Challenges and Controversies
Speedy deletion’s immediacy means legitimate content possibly flagged incorrectly can disappear before creators even notice. For example, a basic draft of an emerging business leader that omits key references might vanish overnight, leaving little opportunity to intervene.
Additionally, different admins might interpret the criteria slightly differently, leading to occasional uncertainty. The preventive solution here is to ensure careful, proactive compliance with Wikipedia guidelines from the start.
Proposed Deletion (PROD): Encouraging Collaboration
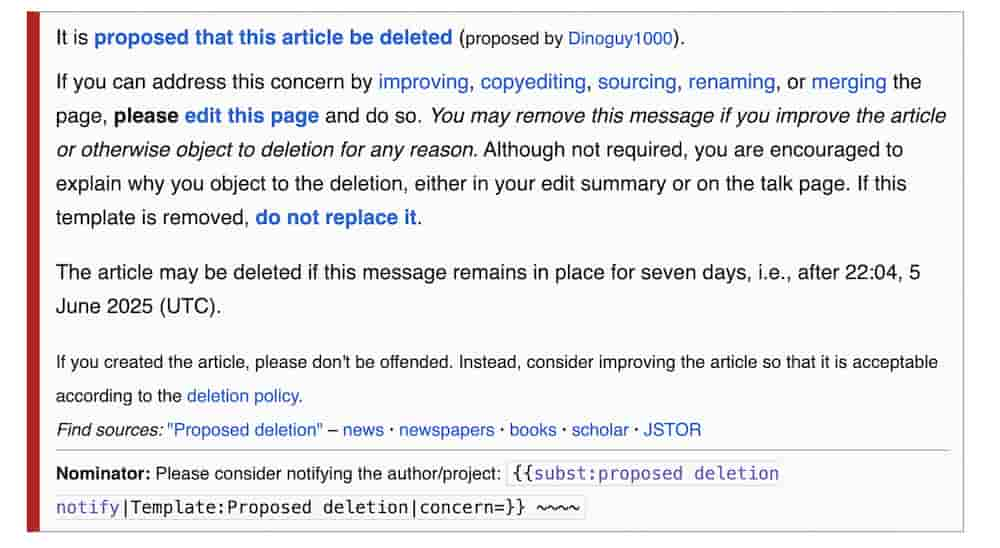
PROD strikes a middle ground—allowing time and encouraging collaboration before content removal. This Wikipedia deletion process works best for articles that need improvement, rather than outright deletion.
Understanding PROD
Editors propose deletion of articles lacking compliance (e.g., not enough references), tagging them for improved sourcing. This launches a one-week “grace period” during which any Wikipedia editor can fix shortcomings or contest removals outright.
Consider a case where a mid-sized nonprofit’s page doesn’t clearly show coverage in independent media sources. During PROD’s seven-day timeframe, PR representatives or engaged editors can provide stronger references to prove notability and preserve the entry.
Benefits of PROD
The PROD process provides structured collaboration. Instead of enforcing immediate removal, it offers contributors an important chance to make substantive improvements. This tends to be effective for corporate and personal biography entries.
Downsides of PROD
On the downside, PROD notifications can sometimes go unnoticed, especially by casual creators. Articles then vanish quietly after seven days. Vigilance and proactive monitoring become essential for organizations concerned about Wikipedia visibility—another reason why keeping track of your online presence matters.
Articles for Deletion (AfD): Debate and Consensus

AfD invites extensive community deliberation—ideal for gray-area articles whose notability or relevance is legitimately disputable.
The AfD Process
A nominated article kickstarts public debate, with editors discussing the entry’s merits and possibly proposing fixes. This democratic forum assesses sources, coverage, and topic legitimacy over roughly a week.
For example, a software startup’s article, nominated due to initially weak media coverage, can withstand AfD if creators present evidence of recent, detailed third-party reporting.
Advantages and pitfalls of AfD
The transparent, democratic process ensures fair evaluations, offering article defenders ample opportunity to present evidence. But it requires attentiveness—it can become contentious, and niche articles may struggle if participants lack familiarity with specific industries or topics. It’s a reminder of the value of communicating clearly and thoughtfully in the Wikipedia deletion process.
Practical Implications: Choosing the Right Deletion Method Matters
Selecting the wrong deletion pathway could upset overall content harmony, negatively impact organizational rapport within the Wikipedia community, or create public debates that highlight organizational weaknesses.
Proactively monitoring articles, promptly addressing concerns, and thoughtfully choosing PROD or AfD rather than Speedy Deletion, where applicable, help nurture positive interactions and drive strategic improvements. Doing so reinforces your organization’s credibility while respecting Wikipedia’s goals.
What to Do If Your Wikipedia Page Is Tagged for Deletion
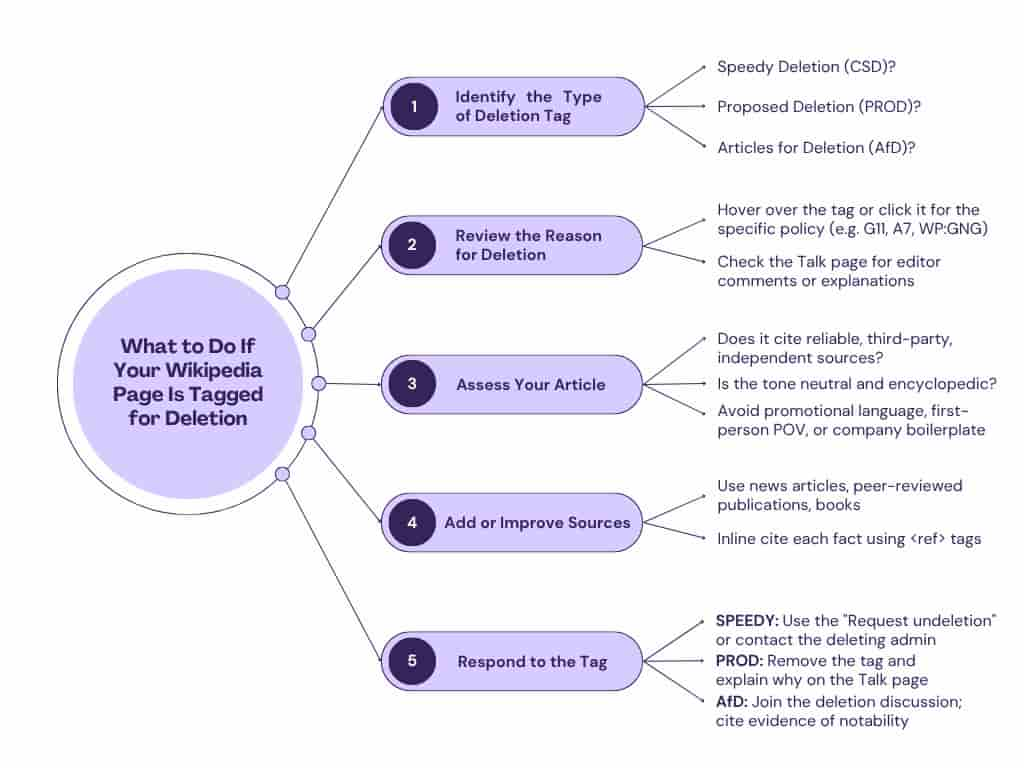
Why Deletion is a Reputation Risk
A deleted Wikipedia page doesn’t just disappear. It can damage your brand’s perceived legitimacy. For most people and search engines, Wikipedia equals credibility. Losing that presence (especially for executives or public-facing brands) sends a powerful message: “This person or organization isn’t notable.”
Connecting Back to Wikipedia’s Purpose: Article Integrity
Whichever deletion path you encounter, aligning proactively with policy significantly reduces risks. Adhering consistently to Wikipedia’s sourcing, neutrality, and encyclopedic standards ensures stronger, more lasting content. By treating deletions as opportunities to continuously clarify and refine your information, you become an authentic partner in Wikipedia’s mission, both protecting and strengthening your online presence over time.
