Online Defamation: A Response Blueprint

Online defamation refers to false statements about an individual or business that harm their reputation. It spans many platforms, including social media, blogs, and online forums, making online reputation management a big concern for many. This article provides an explanation of various types of online defamation and actionable responses.
The process of navigating online defamation involves understanding its nature—predominantly libel in the online context, which concerns written or published false statements that damage reputation.
Defamation can be either libel or slander. Here’s the difference between the two:
- Libel: A written or published defamatory statement.
- Slander: Defamation that is spoken.
To be considered defamation, the material must be:
- Demonstrably false
- Shared with a third party
- Harm the subject’s reputation or financial standing
In response to this daunting yet increasingly common challenge, this article provides a comprehensive blueprint for individuals and businesses to follow.
Table of Contents
What is Online Defamation
Online defamation is any false statement about an individual or business that is published online and can cause harm to their reputation.
Here’s a breakdown to elucidate the concept further:
- Definition and Types:
- Defamation: A false and unprivileged statement of fact that is harmful to someone’s reputation, made with fault, such as through negligence or malice.
- Online Defamation (Cyber Libel): The publication of false statements of fact about a third party online that causes reputational damage. This can include libel (written defamation) and slander (spoken defamation), manifesting across various platforms such as review sites, social media, and video posts.
- Is it defamation? If you can answer yes to these points, you may be a victim of online defamation:
- The defendant published a statement about the plaintiff to a third party.
- The statement was false and capable of being proven false.
- The statement was not privileged and made with the requisite degree of fault.
- The statement was either inherently damaging or caused economic damage.
- Consequences of online defamation:
- Impacts on Victims: Online defamation can have severe impacts, causing reputational, emotional, and financial harm. It can affect anyone, from celebrities to small business owners and private citizens, leading to emotional distress, professional harm, and financial loss.
- Legal Consequences for Perpetrators: This may include civil liability or lawsuits, possible criminal charges, and reputational consequences. Specific legal requirements and defenses vary by jurisdiction, such as the truth as an absolute defense and the significance of opinions.
- Preventive Measures and Response: Identifying the publisher, preserving defamatory content as evidence, and reporting the content to the platform or website are critical first steps. Additionally, avoiding public disputes online and claiming social media profiles can help prevent online defamation.
Understanding these elements is crucial for individuals and businesses navigating the complexities of online defamation. It not only aids in recognizing defamation but also informs the steps necessary to implement preventive measures effectively or, if all else fails, take legal action.
Identifying Defamatory Content
Identifying defamatory content online is a critical step towards seeking help with online defamation and effectively managing one’s online reputation.
This process involves several key elements that must be thoroughly understood and assessed:
- Validity of the Statement:
- It’s imperative to establish whether the statement in question is entirely false. A statement must convey a provably false factual assertion to be considered defamatory, such as allegations of criminal activity or unethical behavior without any basis in truth.
- Publication and Audience:
- For content to be deemed defamatory, it must have been made publicly available to someone other than the person defamed. This includes posts on social media platforms, website comments, and articles on online publications. The wider the statement’s audience, the greater the potential for reputational harm.
- Impact on Reputation:
- The content must be shown to negatively impact your reputation. This involves demonstrating that the false statement has led to tangible harm, such as loss of business, professional discredit, or personal distress.
- Privilege and Fair Comment:
- Certain statements are protected under the principle of privilege, such as fair comments about public proceedings. It is crucial to determine whether the statement falls under any legal protections that might exempt it from being classified as defamatory.
- Legal and Factual Analysis:
- Distinguishing between fact and opinion is vital, as opinions can also be defamatory if they imply an assertion of verifiable fact that can harm one’s reputation. Legal advice may be necessary to navigate these complexities.
- Identifying the Responsible Party:
- Identifying who is responsible for the defamation is crucial, especially in cases where pseudonyms or anonymous profiles are used. Once you determine something is fake news or authored by trolls, you can create an effective plan.
By meticulously evaluating these factors, individuals and businesses can better understand whether they are facing online defamation and decide on the appropriate steps for response and resolution.
Online Reviews as Defamatory Content
Businesses often face anonymous or fraudulent negative reviews on review sites. These can include false claims about the business, its products, or services, leading to potential defamation lawsuits if the claims are demonstrably false.
Google My Business is a vital tool for businesses seeking to manage their online reputation. A crucial aspect of maintaining a positive online reputation is addressing and reporting fraudulent reviews that can harm your business’s image.
Here’s how to navigate this process effectively.
What Google Considers Fraudulent
Google defines fraudulent content as fake, dishonest, or misleading content.
Reviews must be based on real experiences and information. The company explicitly prohibits:
- Fake content: Reviews should reflect genuine customer experiences. Fabricated reviews, whether positive or negative, are not allowed.
- Impersonation: Assuming the identity of another person or organization to post a review is prohibited.
- Conflict of interest: Posting reviews about your own business or a competitor’s business to manipulate ratings is not acceptable.
- Off-topic content: Reviews must be relevant to the actual experience with the business. Irrelevant content, including political or social commentary, is not considered appropriate for review sections.
- Restricted content: Reviews should not contain or link to content that violates Google’s policies, such as illegal or sexually explicit material.
- Spam: Repeated or unwanted content that aims to manipulate a business’s ratings is prohibited.
Understanding these guidelines is the first step in identifying and reporting reviews that may harm your business’s reputation on Google. For a full list of Google’s Prohibited & restricted content, click here.
How to Report Fraudulent Google Reviews
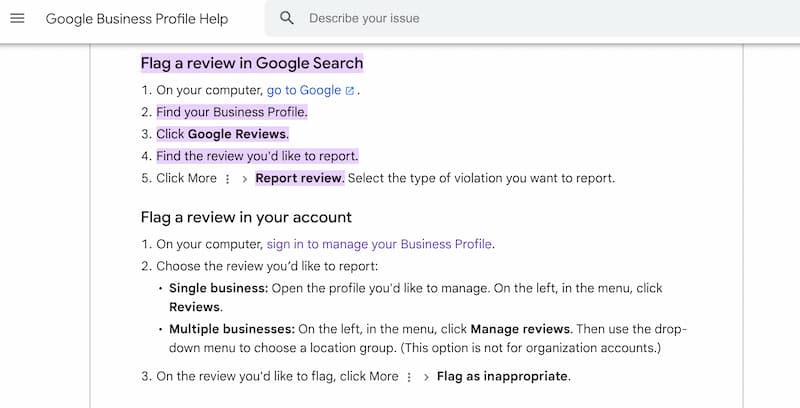
- Identify the fraudulent review: Be vigilant and regularly monitor your Google My Business profile to quickly identify any suspicious or clearly fraudulent reviews.
- Report to Google: Once you’ve identified a fraudulent review, you can report it directly through your Google My Business account. Click on the review you wish to report and select the ‘Flag as inappropriate’ option. This signals to Google that the review may violate their posting guidelines.
- Provide evidence: If possible, provide evidence to support your claim that the review is fraudulent. This could include inconsistencies in the reviewer’s account details or history, clear deviations from actual customer experiences, or evidence of malicious intent.
- Follow up: After reporting, monitor the status of your report. Google may take several days to review and respond. If the fraudulent review remains or if you face a significant number of fraudulent reviews, consider reaching out to Google’s support team for further assistance.
- Engage professionally: In cases where a review is negative but not clearly fraudulent, it’s often best to respond professionally and constructively. This shows other potential customers that you take feedback seriously and are committed to improving your service. Check out our guide to replying to negative reviews here.
Social Media as Defamatory Content
With the ever rising popularity of social media, the risks and impacts of defamation are impactful:
- An estimated 5.17 billion total social media users worldwide in 2024.
- The average person uses 6.7 different social networks per month.
Platforms like TikTok and Facebook often do not remove content unless it violates their guidelines, leaving victims with limited recourse. Take social media impersonation (fake social media accounts pretending to be someone else), the bar is high for removal. When we at Reputation X remove fake social media accounts, we often feel like we are shouting into the void.
Social media platforms are ripe for defamation, from false accusations of misconduct by ex-partners to competitors making misleading statements about products or services. The vast reach of social media exacerbates the potential damage.
Despite the harm caused, most social media companies are shielded from liability for user-posted content under Section 230(c) of the Communications Decency Act, complicating efforts to have defamatory content removed.
On social media, defamation can occur through various means, including:
- Posts
- Comments
- Videos
- Shares
Social media’s viral nature can amplify defamatory content’s impact, spreading it rapidly across platforms and causing significant reputational damage.
Key Characteristics of Defamation on Social Media Include:
- Virality: Information on social media can spread quickly and widely, often without context, leading to rapid damage to reputation.
- Anonymity: People often feel emboldened to post harmful content anonymously or under pseudonyms, complicating accountability.
- Permanency: Once defamatory content is published online, it can be difficult to remove, persisting in search results and social feeds.
Managing Defamatory Social Media Content
- Monitoring and Identification: Regularly monitor social media channels for mentions of your brand or name to identify potential defamatory content quickly.
- Legal Evaluation: Consult with legal professionals to determine if the content meets the legal defamation criteria and understand your options for recourse. Keep in mind that public figures often face higher thresholds for proving defamation, as they must also demonstrate actual malice or reckless disregard for the truth.
- Content Removal Requests: If the content is defamatory, request its removal from the social media platform. Most platforms have policies and procedures for reporting and removing such content.
- Response Strategy: Develop a communication strategy to respond to defamatory content. This may involve public statements, clarifications, or outreach to affected parties.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of the defamatory content, your communications, and actions taken, as these can be important in legal proceedings.
- Reputation Repair: Implement a reputation management strategy to mitigate the impact of defamatory content, which may include SEO tactics, positive content creation, and public relations efforts.
Real-World Example: The Case of Lisa-Michelle Kucharz
Lisa-Michelle Kucharz’s experience is a stark reminder of the damage that online defamation can cause. Kucharz was targeted by a stranger who posted false accusations against her on various social media platforms and blogs.
These unfounded claims not only caused her emotional distress but also had profound effects on her professional life and financial well-being. Her case underscores how defamatory content can severely impact an individual’s reputation and quality of life, especially when spread across multiple platforms.
Steps to Take When Faced with Online Defamation
When faced with online defamation, a strategic and measured approach is essential for effective resolution and minimizing damage to your reputation. Most importantly, stay calm during this uncomfortable situation. Then, consider the following options:
Immediate Actions
These immediate actions should be taken in every instance of defamation, no matter how small or large. Everyone can start right here.
- Stay Calm and Assess the Situation: Avoid quick, emotional reactions that may exacerbate the issue. Carefully evaluate the content and its potential impact on your reputation.
- Collect Evidence: Document the defamatory content. Use tools or methods to create authenticated copies of the posts, articles, or comments. This is essential if the situation ever reaches a court case.
- Report the Content: Utilize the reporting features on the platform where the defamation occurred. Most websites and social media platforms have policies against such content and may take it down upon review.
Reputation Management
Reputation management strategies work best when tailored to your specific situation. Everybody’s plan will be different and dependent on several factors, such as the type, severity, and source of defamation, as well as your own online presence.
- Respond Publicly When Appropriate: In some cases, a public response may be warranted to clarify inaccuracies and present your side of the story. Ensure responses are professional and fact-based.
- Engage Online Reputation Management Services: Professionals in reputation management can assist in suppressing negative content through strategic use of SEO and content creation, thereby mitigating the impact of defamation.
- Monitor Your Online Presence: Regularly check for defamatory content on social media, review sites, and search engine results. Early detection allows for quicker responses and lessens potential damage.
Legal and Professional Steps
Legal actions should be reserved as a last resort. Remember that any legal actions you take can, in fact, backfire and make any threats to your reputation even more impactful.
- Seek Legal Advice: Consult with a defamation lawyer to understand your options and the best course of action. This may include drafting a cease and desist letter or pursuing litigation if necessary.
- Send a Cease and Desist Letter: A formal demand from a law firm may prompt the removal of the defamatory content. This step signals the seriousness of your intent to protect your reputation.
- Pursue Legal Action if Necessary: If the defamation persists and causes significant harm, filing a lawsuit might be the appropriate response. Legal action can seek the removal of the content and compensation for damages.
Best Practices for Responding to Defamation
Adopting a strategic and comprehensive approach that encompasses preventive measures and responsive actions is essential in addressing online defamation. Here are some best practices:
Preventive ORM Measures
- Guidelines and Policies: Establish clear guidelines for customers wishing to leave reviews, explicitly condemning the use of defamatory statements or false claims. This proactive step can deter malicious content at the source.
- Automated Monitoring: Utilize automated tools or engage professional services to regularly monitor your online reputation. Early detection of potential defamation allows for a swift and more effective response.
- Content Creation: Regularly produce and disseminate positive content about your strengths and achievements. This enhances your online presence and helps dilute any negative content’s impact.
- Encourage Genuine Reviews: Actively encourage customers to share their genuine experiences. A robust collection of positive reviews can significantly reinforce trust and mitigate the effects of a few negative comments.
Response Strategy
- Develop a Response Plan: Craft a clear and concise plan for dealing with defamation, ensuring that your communication is professional and effective. This plan should include steps for both immediate and long-term actions.
- Lawsuit Considerations: Filing a lawsuit is a significant move and should be considered carefully. Factors such as the prior strength of your reputation and the availability of time and money should be considered. Be mindful of the potential for the Streisand Effect, where legal action can inadvertently draw more attention to the defamatory content.
How Can We Help You?
From negative content removal to suppression, correction, and ratings and review management, our experts can solve nearly any online brand issue.
What steps should be taken if someone defames you on social media?
Managing online defamation effectively is crucial in protecting your personal or professional reputation. Here are the steps you should take if you find yourself defamed on social media: document the defamation, assess the situation, attempt to resolve it directly, contact the social media platform, respond publicly if necessary, engage legal help, strengthen your online reputation, and consider reputation management services.
Can you explain what defamation entails?
Defamation involves spreading false statements about an individual that can harm their reputation. These statements are not based on truth and are disseminated with the intent to degrade someone’s respect, reputation, or induce unfavorable opinions against them.
What constitutes as slander on the internet?
With the surge in social media usage, online defamation, which includes slander, has become more prevalent. Slander refers to defamation that is spoken, whereas written defamation is known as libel. Regardless of the form it takes, defamation on the internet involves making false statements that damage someone’s reputation.
