How to Avoid the Corporate Pitfalls of Online Reputational Risk
What is reputation risk, and how to reduce it
Reputational risk is finally starting to gain some traction among executives and decision-makers as a legitimate and essential part of their business strategy.
Considering the massive and sometimes devastating effects of reputation damage, it’s a wonder there are still so many businesses leaving themselves vulnerable.
Learn more about what reputational risk is, where it comes from, and how you can protect your company from the losses it causes.
Sections
- What does “reputational risk” mean?
- What is reputation damage?
- What causes reputational risk?
- How do you measure reputation risk?
- What is reputation risk management?
What does “reputational risk” mean?
Reputational risk or reputation risk is anything that threatens the reputation of your company, institution, or organization.
Corporate reputation is directly linked to shareholder value, revenue, recruiting, and investor interest and should therefore be carefully managed.
There are two types of reputational risk to watch out for: direct and indirect. In either case, reputational risk can arise seemingly out of nowhere and cause severe, irreparable damage to even the largest, most well-established, and most admired companies. Damage caused by reputational risk has been known to cause the loss of millions or even billions of dollars in revenue and market capitalization.
Direct reputational risk
Direct reputational risk is risk created as a direct result of deliberate action or inaction of the company regarding established and evolving standards of employment, governance, social responsibility, and more.
While direct reputational risk presents far more opportunities for damage than indirect reputational risk, both are prevalent and should be mitigated to the best of a companies’ ability.
Indirect reputational risk
Indirect reputational risk can be caused by the negligence or deliberate action of employees or tangentially through peripheral parties.
This type of risk is unintentional from the company’s perspective, but the damage can be just as severe because the risk puts a spotlight on the inability or unwillingness of the company to prioritize risk mitigation and security or otherwise manage their employees and affiliations.
What is reputation damage?
Reputational risk causes a ripple effect that is sometimes quickly recoverable and other times is catastrophic. Damage caused by reputational risk is known as reputational damage or reputation damage.
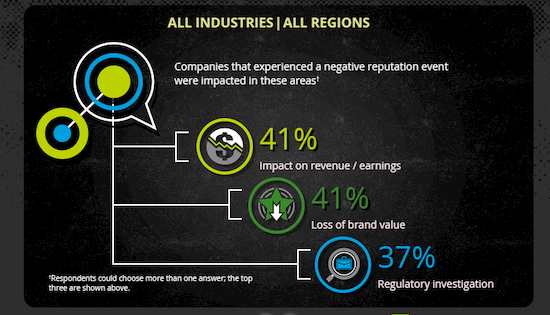
Reputation damage is measured in lost revenue, increased operating costs, increased capital and regulatory costs, and loss of shareholder value, but it can affect virtually every aspect of a business.
In a 2013 survey conducted by Deloitte, 87% of executives rated reputational risk as either “more important” or “much more important” than other strategic risks because of the potential consequences of reputation damage.
Potential impact of reputation damage
- Loss of revenue from existing customers
- Loss of volume of existing customers
- Reduced ability to attract new customers
- Reduction in share price
- Reduced ability to invest
- Reduced valuation for mergers and acquisitions
- Loss of vital staff
- Reduced recruiting ability
- Aggressive competitor takeover
- Increased compliance
- Negative brand perception
- Negative media coverage
- Employment conditions
- Executive compensation
- Product quality relative to price
- Working practices across supply chains
- Customer privacy and security
- Product recalls
- Fraud and corruption in foreign market subsidiaries
- Conflict of interest and difficulty with regulatory changes
- Financial or reporting irregularities
- Tax avoidance and tax evasion
- Scrutiny of business practices from stakeholders and media
- Social responsibility
- Discrimination
- Excessive cost-cutting maneuvers
- Inappropriate credit decisions
- Questionable investments
- Earnings not meeting expectations
- Employee error or negligence
- Physical security breach
- IT breach
- Social media posts and behavior
- Any direct reputation risk executed by affiliates or employees
What causes reputational risk?
We live in a society that is connected to everything at all times. Information is more easily accessible today than ever before, and less easy to verify. Without taking deliberate steps to address potential reputational risk and avoid reputational damage, virtually any company or organization can fall victim to the effects at any time.
Direct causes of reputational risk
- Employment conditions
- Executive compensation
- Product quality relative to price
- Working practices across supply chains
- Customer privacy and security
- Product recalls
- Fraud and corruption in foreign market subsidiaries
- Conflict of interest and difficulty with regulatory changes
- Financial or reporting irregularities
- Tax avoidance and tax evasion
- Scrutiny of business practices from stakeholders and media
- Social responsibility
- Discrimination
- Excessive cost-cutting maneuvers
- Inappropriate credit decisions
- Questionable investments
- Earnings not meeting expectations
Indirect causes of reputational risk
- Employee error or negligence
- Physical security breach
- IT breach
- Social media posts and behavior
- Any direct reputation risk executed by affiliates or employees
How do you measure reputation risk?
There is no way to put a number on the amount of risk your company could potentially incur because there are virtually infinite opportunities for reputational risk and damage.
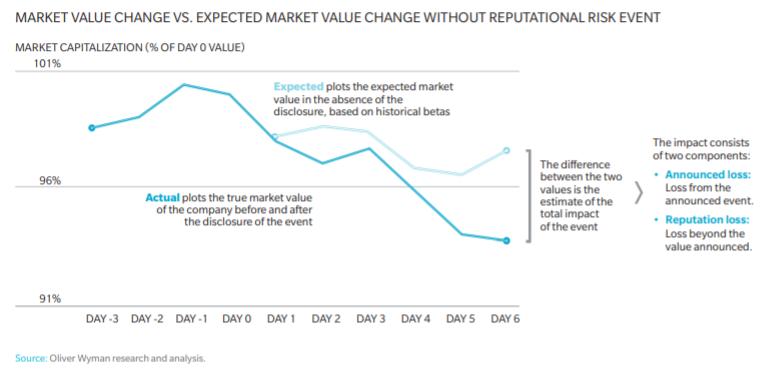
Once a risk event has occurred, you can quantify the risk. Quantifying reputational risk can be done in four steps.
First, a business needs to identify the potential for reputational risk damage. Then, estimate what its stock performance would be if the event had not occurred. Compare that estimate with actual stock performance. The difference is your reputational risk impact.
Identify the potential for loss
Any event that has a potential effect on reputation can be assessed for reputational risk as long as:
- The event is related to a publicly listed company that has a relevant index to compare stock performance,
- the event date is known, and there is no indication of a leak, and
- The announced financial loss has a noticeable impact.
Estimate hypothetical stock performance
Using historical stock betas, estimate the would-be stock performance (as if the event didn’t happen). Continue to track the market in the days following the event for future comparison.
Compare hypothetical and actual performance
Calculate the difference between the hypothetical estimate and the actual stock performance for ten days after the event. Ten days is a good window because it’s long enough to encompass the impact and short enough that additional factors won’t begin to skew the results.
Determine impact
Compare the actual loss relative to the hypothetical performance versus the loss announced due to the event. The difference can be attributed to reputational risk if the actual loss is greater.
The reputational damage might be due to market suspicion of the company underestimating the potential loss. In a study of risk events, more than 55% of events had a reputational impact.
What is reputation risk management?
Reputational risk management is when a company mitigates its reputational risk by identifying, assessing, and controlling threats to its reputation and, thereby its market value and revenue.
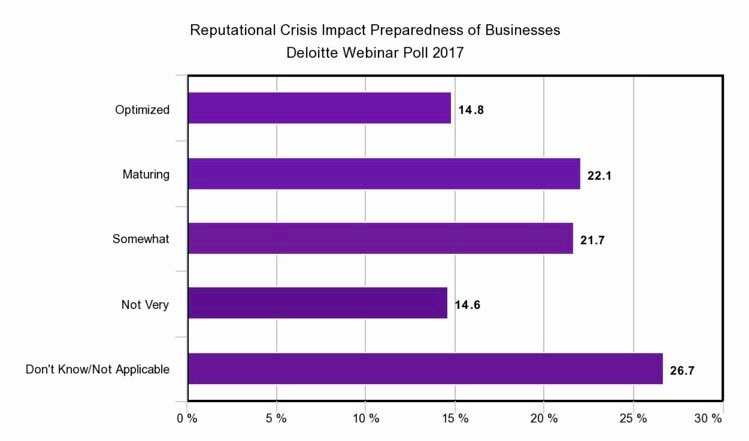
Reputational risk is arguably the most unpredictable type of risk to a business or organization and should, therefore, be managed as strictly as possible, but many companies admit they are unprepared.
About 44% of companies see themselves as “somewhat” prepared or “maturing” in their preparedness. Less than 15% feel their reputational risk mitigation is “optimized,” and a similar number feel their reputational risk mitigation is inadequate.
Begin the process by performing a reputational risk assessment. Segment your stakeholders and evaluate their perception of key company factors such as financial performance, leadership, social responsibility, and work environment. You can check external perception and risk factors by analyzing the quantity and density of unfavorable content and discussion topics in Google’s index. Develop a strategy based on the type of exposure your company is facing. Work with a PR firm or crisis management team to resolve active crises.
Reputational Risk Insurance
There are reputational risk insurance providers such as Steel City RE. Firms like Steel City work with companies, for the most part, rather than people. Examples of services include predicting reputational risk, enterprise value protection, and promoting risk management.
Internal Reputational Risk Mitigation
Most reputational risk mitigation happens within the company itself. To reduce the potential for reputational risk, the Board of Directors should be active in the development, execution, and enforcement of reputational risk strategies, which should be integrated into business planning.
Maintaining strong and well-established corporate values can help mitigate indirect reputational risk. Policies and procedures related to ethics and compliance should start at the top and be taught as part of company culture. All stakeholders, from employees to customers and shareholders, should have a positive experience with the company as a priority.
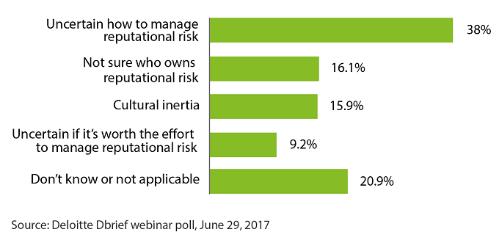
Survey of Executives on Reputational Risk Mitigation
Deloitte Debrief webinar poll, June 29, 2017
Any and all public reporting and financial statements should be accurate and of high quality. Discrepancies are noticed by investors and reflect poorly on the company. Reporting, operations, and compliance should be carefully controlled in the interest of company objectives. A competitive business model is essential to maintaining a reputation as a competent leadership team. Finally, planning and execution of crisis response will have a significant impact on your reputation and related risk and should, therefore, be a high priority.
Online Reputation Management
Your online presence greatly contributes to your overall corporate reputation and often has a hand in reputational risk. A professional online reputation management firm can get a handle on your social media, content, outreach, digital assets and creation, SEO, and brand management. Strategic marketing campaigns can amend a negative narrative to repair damage.
Reputation Risk FAQs
Is reputational risk part of operating risk?
Operational risk is the potential for loss caused by failed internal processes, systems, people, or external events. Strategic risk and reputational risk are not part of operating risk.
What is reputational risk in banking?
Reputational risk in banking is similar to that of reputational risk in other sectors. Reputational risk from direct or indirect actions can damage a bank’s brand and reputation, causing severe damage to earnings and value. The 2016 Wells Fargo incident is a prime example of direct reputational risk in banking.
What is reputational risk insurance?
There are insurance policies built to protect companies from damages caused by reputational risk. These policies typically cover compromised customer data, social media activity that results in negative reputation effects, and other direct reputational risk behaviors.
Tags: Business Reputation Repair, Corporate Reputation, Reputation Management, Reputation Marketing.