How to Remove Personal Information from Search Results
In a perfect world, removing your information from search results would be as easy as dropping a file in a cyber trash can. Unfortunately, the internet is a precarious place, and anything that goes “live” has the potential to spread to other sites and social media profiles.
Here is a diagram that explains, step by step, how to remove information from the web.
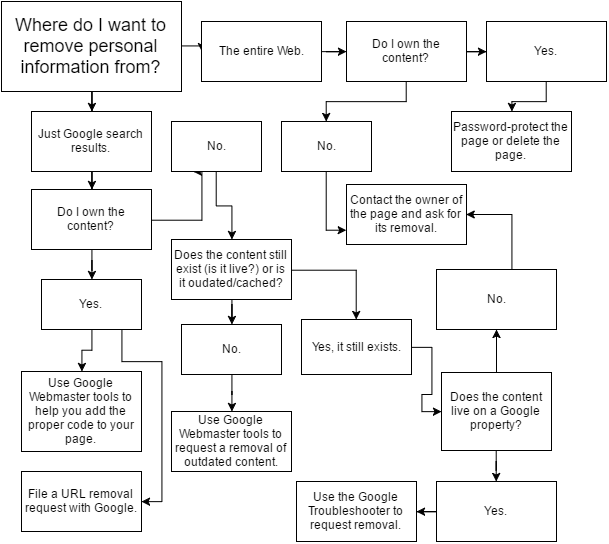
Personal information is more accessible than ever before, often just a few clicks away on search engines like Google and Bing. This accessibility can lead to privacy concerns, as personal details such as home addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses can be easily found online. Understanding how to manage and remove this information is crucial for maintaining privacy and security.
Identifying Personal Information on Search Engines
When using features like Google’s “Results about you,” you can discover if your personal contact information appears in search results [1]. This tool is very good for identifying some of the personal data that you might want removed from public visibility. But it doesn’t cover some of the most damaging results.
Removal Guidelines and Procedures
Google and Bing have specific guidelines for removing personal information. For instance, Google will not remove information deemed valuable to the public, such as content from government or educational websites and online newspapers [1]. But, if the information meets certain criteria—such as being a direct risk to your privacy without public value—it may be eligible for removal. You can submit a removal request, and if it adheres to these guidelines, the information might be removed entirely or just from queries that include your name [1][3].
Challenges in Removal Requests
Not all removal requests are successful – according to our clients, most are not. If a request is denied, which is common, search engines typically provide a reason, allowing you to understand why the information remains online [1]. This feedback can be useful for reassessing your approach if you should choose to resubmit the request or seek alternative removal methods (see below).
What Google and Bing May or May Not Remove
What Can Often Be Removed
Google and Bing often approve removal requests for certain types of sensitive information. This includes:
- Personal contact information such as phone numbers, home addresses, and email addresses [12][15].
- Confidential government identification numbers, bank account details, and images of signatures or ID documents [15].
- Outdated or irrelevant content that no longer serves the public interest but could harm personal privacy [14].
For Bing, users are advised to also contact the websites directly where their personal information is displayed. This ensures the removal of data at its source, which subsequently leads to its removal from Bing’s search results [20].
What Can Often Not Be Removed
Despite the provisions for removing sensitive data, there are limitations to what Google and Bing can remove:
- Information that is considered newsworthy, professionally relevant, or of significant public interest will generally not be removed. This includes content from government and educational institutions, as well as news outlets [12][15].
- Personal information that appears in public records or other official documents can also be difficult to remove unless it falls under specific privacy risk categories [15][20].
Identifying Personal Information on Google
Types of Personal Information
Personal information that can appear on Google and may be subject to removal includes your home address, phone number, and email address. This type of information can be found by searching your name along with your home city or address [22]. Google uses this data to identify search results that display personal contact information [22]. If you discover such information in the search results and prefer to keep it private, you have the option to request its removal [22].
How to Use Search Functions to Find Information About You

To search for your personal information on Google, you can try the “Results about you” feature first. This involves searching for combinations of your name with other personal identifiers such as your city or home address [22]. Google processes this information to check for search results that display your personal details [22]. If negative results are found, you can initiate a removal request directly right through Google’s interface [22].
Some Results May Be Worse Than Others
Name in Headline
Having your name in the headline of an article will often translate to having your name in the Google search results, and it can significantly impact your online reputation. This visibility often leads to increased visibility – showing up more highly in search results than other results without your name in the headline. That’s why one of the methods we recommend is to ask friendly, or somewhat friendly authors, to at least remove your name from the headline if you can get them to.
Frequently Updated Content
If your personal information is included in content that is frequently updated and widely regarded as valuable, such as news articles or official records, it is more likely to appear prominently in search results [22][29]. This is one of the reasons negative content on places like Reddit.com can be so challenging to remove. This increased visibility can make it more difficult to manage your online privacy effectively.
Powerful Websites
An article in the New York Times with your name in the headline is incredibly difficult to remove. Not only is the name in the headline, but the New York Times, and many other online publishers have a powerful presence on the web. They are preferred by search engines, so they rise in visibility. The worst kind of visibility.
By understanding the types of personal information that can appear on Google, utilizing search functions effectively, and recognizing the implications of having your name in headlines and the relevance of articles, you can better manage your online presence and take steps to safeguard your personal information [22][29].
Utilizing Google’s ‘Results About You’ Feature
Setting Up Alerts
Google’s “Results About You” tool allows you to set up alerts to monitor when your personal information, such as your email, home address, and phone number, appears in Google Search results. So it is helpful for some limited cases. But Results About You will not help with a negative blog post, article, video or reviews. To begin, log into your Google account and navigate to the specific page for the tool, here. This is where you start, and where you can add the personal information you want Google to track. Once added, you can choose how you’d like to receive notifications—via email or push notifications on your linked devices. This proactive approach helps you stay informed about your online presence [52][56][58].
Here is an example:
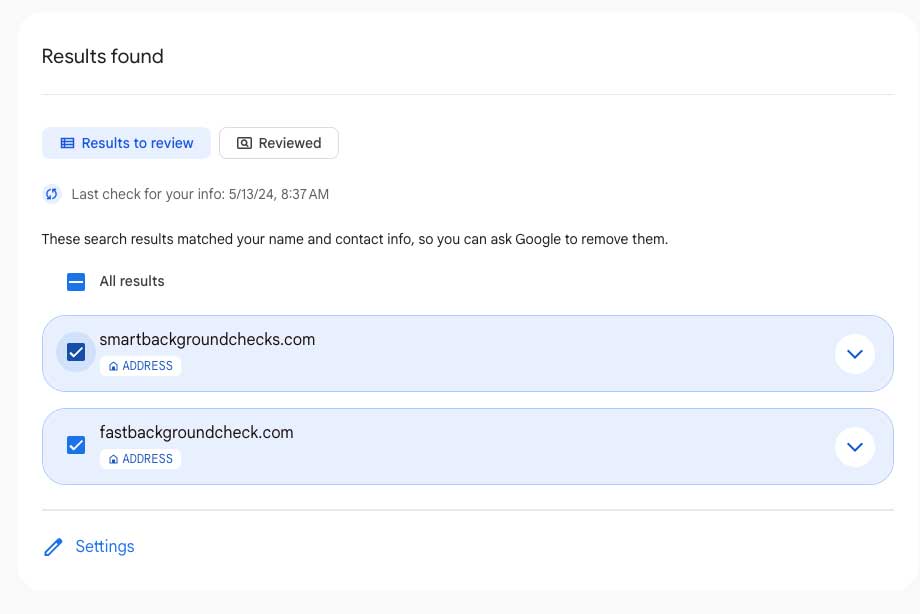
When Google finds something that may have your personal information, it will show up on this page. Then, at the bottom, click Request to Remove.
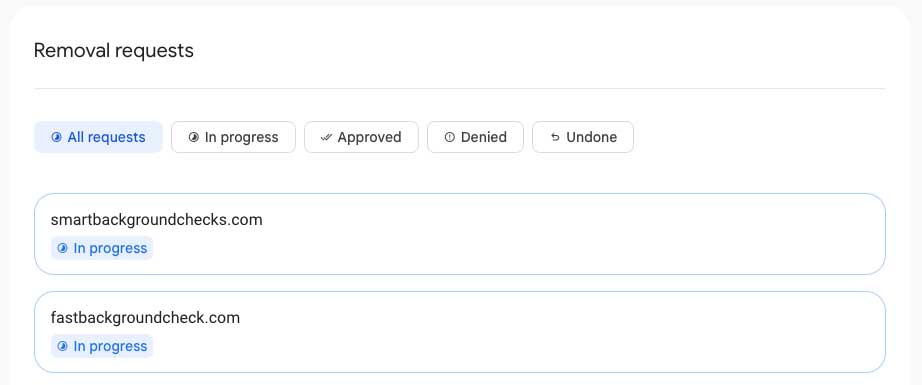
Submitting Removal Requests
When you identify personal information in search results that you wish to remove, Google’s “Results About You” feature provides a streamlined process for submitting removal requests. This is what a request looks like once it has been initiated:
When to Use Google’s Results About You
“Results About You” is useful when personal information is displayed without your consent, potentially leading to privacy concerns or identity theft. This tool is also beneficial for managing how your personal data is viewed publicly, allowing you to request the removal of sensitive information like social security numbers, login credentials, or explicit images that have been shared without your permission [55][56][58].
Limitations to Google’s Results About You
It’s important to understand the limitations of the “Results About You” feature – and there are a lot of them. While it can remove personal information from Google’s search results, it does not delete the information from the internet or the original source. If the content resides on a website that Google does not control, you may need to contact the website’s owner or administrator directly to request removal. You can also contact the author or blogger. This is discussed in more detail below.
Legal and Policy Considerations
What Google and Bing Will Remove
Google and Bing have specific guidelines that dictate the types of content they will remove from their search results. This typically includes personally identifiable information (PII) that could lead to identity theft, financial fraud, or other significant harms. Explicit or intimate images shared without consent also fall under this category and are eligible for removal upon request [62][67]. Additionally, content that violates local laws or Google’s content policies may be removed or restricted in the specific region where it is deemed illegal [72].
Documents You May Be Asked to Provide
When submitting a removal request, you may need to provide specific documents to support your claim. This could include a copy of a government-issued ID, legal documents pertaining to a court order, or other relevant evidence demonstrating the content’s violation of laws or terms of service. Google and Bing require these documents to verify the authenticity of the request and to ensure that they comply with legal standards [62][80].
Handling Denied Requests
If your request to remove content is denied (again, common), it’s important to understand the reasons behind the decision. Common reasons include the content not being found in Google’s index, the content is not the type they remove, or the request being a duplicate of a previous one. Understanding these reasons can help you adjust your approach, such as contacting the webmaster directly to remove the content or updating your request with accurate information [77].
The Difference Between Defamation and Libel
Defamation involves the publication of false information that harms a person’s reputation. Online, this is often referred to as internet defamation and can include harmful false statements made via websites, social media, or other digital platforms. Defamation is categorized into libel, which is written defamation, and slander, which is spoken [66][67].
Libel is a form of defamation that occurs in written form. This includes false and damaging statements published online or in print. Removing libelous content often requires a court order, especially when the information is deeply entrenched in search engine results or hosted on platforms that do not easily comply with removal requests [67].
When Should You Use a Lawyer to Get Content Removed?
Legal intervention is often expensive but necessary when dealing with stubborn or complex cases of online defamation or when personal information is maliciously shared (a practice known as doxxing). A lawyer can help you navigate the legal landscape, file a lawsuit if necessary, and obtain a court order for the removal of the offending content. This is particularly important when the publisher of the content is anonymous or the content has legal ramifications [66][67][80]. Google and Bing will often remove content based on a court order, but getting the court order is the difficult part due to the intricacies of defamation law colliding with freedom of speech.
Alternative Methods for Removing Information
How to Use Terms of Service to Your Advantage
When dealing with unwanted personal information on search engines like Google and Bing, understanding and utilizing their Terms of Service (ToS) can be crucial. The ToS often outlines the types of content that can be removed upon request. For example, Google’s policies allow for the removal of personally identifiable information (PII) if it poses significant risks of identity theft, financial fraud, or other harm [15]. Similarly, Bing encourages users to report content that violates their privacy rights through their “Report a Concern” tool [11].
At Reputation X, we suggest reading the terms of service (ToS) of the platform you want the information removed from as a first step.
Contacting Webmasters
Google and Bing will often deny requests to remove information from search results. The next step is often to initiate the process of removing your personal information from a website, the first step is often to contact the webmaster directly. You can usually locate a “Contact Us” link or an email address on the site’s homepage [82]. If direct contact information is not available, a Whois search can provide details about the website’s owner. Just go to the Whois form, enter the URL of the website, and if the contact information is not privacy protected, you will have the names and addresses of people who run the website.
Getting the Webmaster to Add a NoFollow Tag
If removing the content entirely isn’t possible, perhaps the author will make the page invisible to Bing and Google. So, another approach is to ask the webmaster to add a “nofollow” tag to links leading to the page containing your personal information. This won’t remove the page from the website itself, but it can reduce its visibility in search results – often dropping completely out of search results [86][87]. It’s important to communicate politely and clearly, explaining how the link is affecting you negatively and suggesting the nofollow solution as a compromise [87].
Contacting Bloggers
When dealing with personal information posted on blogs, reaching out directly to the blogger can be effective. If the blog is active, you might find contact details on the blog itself or through a Whois search. Explain your concerns about the personal information and request its removal. If the blogger is unresponsive, platforms like Blogger have mechanisms for submitting content removal requests [91]. Here is an example of a polite but poignant email that can be sent to a blogger requesting removal or the addition of a noindex tag:
| Subject: Request for Article Review or Modification Dear [Blogger’s Name], I hope this message finds you well. I am writing to discuss an article published on your blog titled “[Article Title].” While I understand and respect your freedom of expression and journalistic endeavors, I am concerned about the content of this article as it pertains to its impact on my life. The article is causing unintended harm and I kindly request its removal. If removing the article is not possible, adding a “noindex” tag to the page prevent it from appearing in search engine results would be a greatly appreciated alternative while still keeping the article live. Your cooperation in this matter would mean a lot to me, and I am more than willing to discuss this further at your convenience. Thank you for considering my request, and I look forward to your understanding and support. Warm regards, [Your Name] |
Contacting Journalists
For articles published by news agencies, the process might involve more formal channels. Contacting the journalist directly, or the editor if the journalist is not responsive, can be a starting point. If the content is outdated or inaccurate, requesting corrections or updates might also be an option. Some news organizations may agree to apply a “noindex” tag to the article to prevent it from appearing in search results although this only works with very small publishers and not that often [92]. In our experience, journalists usually refuse and state freedom of speech, “journalistic integrity”, or they just don’t care about how their work may be negatively affecting your life.
Contacting the Hosting Company
If attempts to contact the webmaster fail, the next step could be reaching out to the hosting company. Hosting companies often have policies against hosting sites that display personal information without consent. Again, check their website and look for banned practices in their ToS. If your rationale fits, provide them with details of the content and your previous attempts to have it removed by the webmaster. Most hosting services will require some proof or documentation of the issue before they can act [82][83].
Using Professional Services
For those who find the process daunting or time-consuming, professional data removal services offer a more hands-off approach. These services specialize in identifying and requesting the removal of personal information across various websites and data brokers. They handle the communication and follow-up, which can be particularly useful for removing information from multiple sources [84][100].
Maintaining Online Privacy and Safety
Regularly Monitoring Your Personal Information Online
To maintain control over your personal information and reputation, it’s essential to regularly monitor your online presence. Conduct periodic searches of your name or personal information to assess what appears online [102]. If you find any inaccurate or outdated information, promptly contact the relevant websites or platforms to request removal or correction [102]. This proactive approach not only helps in correcting misrepresentations but also in managing how you are perceived publicly.
Using Additional Privacy Tools and Settings
Utilizing privacy tools and settings can significantly enhance your control over personal data shared online. Employ privacy software or apps, which are available both as free and commercial services, to manage the information you share [106]. Regularly update your devices and software applications to ensure you have the latest security patches protecting against vulnerabilities [102][106]. Additionally, consider using Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to mask your internet protocol (IP) address, thereby enhancing your anonymity and safeguarding your activities from being tracked [108].
Educating Yourself on Digital Footprint Management
Understanding and managing your digital footprint is crucial for maintaining online privacy. Engage with cybersecurity communities, attend seminars, and follow trusted sources of cybersecurity information to stay informed about best practices and emerging threats [102]. Learn about the implications of your online activities and how they contribute to your digital footprint [103][113]. Implement strategies such as using secure and unique passwords, being cautious with personal information on social media, and adjusting privacy settings on various platforms to minimize unwanted exposure [103][113].
By integrating these practices into your routine, you can significantly enhance your online privacy and safety, ensuring that your personal information remains secure and under your control.
FAQs
How can I get my personal information removed from Bing?
To remove your personal information from Bing, you should first visit the Bing Support page. Once there, fill in your name and email address in the provided fields. Next, you need to choose “Content Removal Request,” “Result Removal,” and “Other” from the drop-down lists under the section labeled “What Type of Problem Do You Have?” This will help you initiate the process to have your data removed.
What steps should I follow to delete my personal information from Google?
To delete your personal information from Google, whether you are using a mobile web browser or desktop, start by logging into your Google account. Click on your Google Account avatar to open the menu, then select “Manage your Google Account” followed by “Data & privacy.” Navigate to “History settings” and click on “My Activity.” Scroll down to the “Results about you” section and select “Manage results about you” to begin the process of removing your personal data.
How can I remove my personal information from the Internet?
Removing your personal information from the Internet involves several steps:
- Secure your online accounts.
- Remove your data from Google search results.
- Request that third-party websites delete your information.
- Delete any old accounts and apps you no longer use.
- Enhance your social media privacy settings.
- Opt out of data broker lists.
- Utilize anti-tracking and privacy-enhancing tools.
What are the steps to remove my personal information from search sites?
To remove your personal information from people search sites, follow these six steps:
- Use a search engine to search for your name.
- Compile a list of people search sites where your information appears.
- Visit each site to locate your information.
- Find the opt-out page for each site.
- Submit an opt-out request on each site.
- Repeat this process for every people search site on your list.
Tags: Business Reputation Repair, Individual Reputation Repair, Online Reputation Repair, Reputation Management, Reputation Protection.
