Measuring Your Company?s Most Valuable Intangible Asset Online
Highlights:
-
Corporate reputation is factoring more and more in a company’s value.
-
A report released by global communications firm Weber Shandwick found that global executives attribute an average of 63% of their company’s market value to their corporate reputation.
-
The wide variety of the factors that contribute to corporate reputation, from work environment and corporate culture, to quality of products and services, to community engagement and environmental responsibility, show the increasingly interconnected relationship between business, society, and human emotion.
-
Ways to measure corporate reputation include the Corporate Reputation Quotient, shareholder value, and Net Promoter Score.
How much is corporate reputation worth?
It’s an age-old question in the corporate PR world: What is the value of a company’s reputation? While there are varying opinions on the answer to this question, they all typically support the idea that corporate reputation is an invaluable asset that heavily affects a company’s bottom line.
But how much does a company’s reputation affect its value?
According to a recent report released by Weber Shandwick, in partnership with KRC Research, called “The State of Corporate Reputation in 2020: Everything Matters Now,” global executives attribute an average of 63% of their company’s market value to their corporate reputation.
That’s nearly two-thirds of a company’s market value being determined by how the company is perceived by stakeholders (i.e. customers, investors, employees, etc.). Those polled for the Weber Shandwick report listed the following as the most influential stakeholders on a company’s reputation:
While corporate reputation’s contribution to a company’s market value varies by country, the markets polled for the report gave a percentage of market value attributed to company reputation that ranged from 47% (UK and Hong Kong) to 76% (Brazil). So, at the very least, about half of a company’s market value is determined by its corporate reputation.
What factors influence a company’s reputation?
There has been a recent trend that has seen companies begin to step outside of their comfort zone and into the realm of political and social issues. Even if their political or societal stances do not particularly have anything to do with the business they conduct, companies are now not only expected to deliver financial gain, they also are expected to make positive contributions in these realms. This is called Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
But market success and lending a positive voice to societal issues are only two of many factors that contribute to a company’s reputation. One of the primary findings from Weber Shandwick’s report was that corporate reputation today is omnidriven, meaning numerous factors contribute to its measurement simultaneously.
Everything matters. From work environment, to quality and safety of products and services, to corporate culture, to community engagement, to environmental responsibility, and beyond, the variety and breadth of the factors contributing to corporate reputation evidence the increasingly interconnected relationship between business, society, and human emotion.
Below are the most common responses global executives gave when rating the biggest factors that affect company reputation:
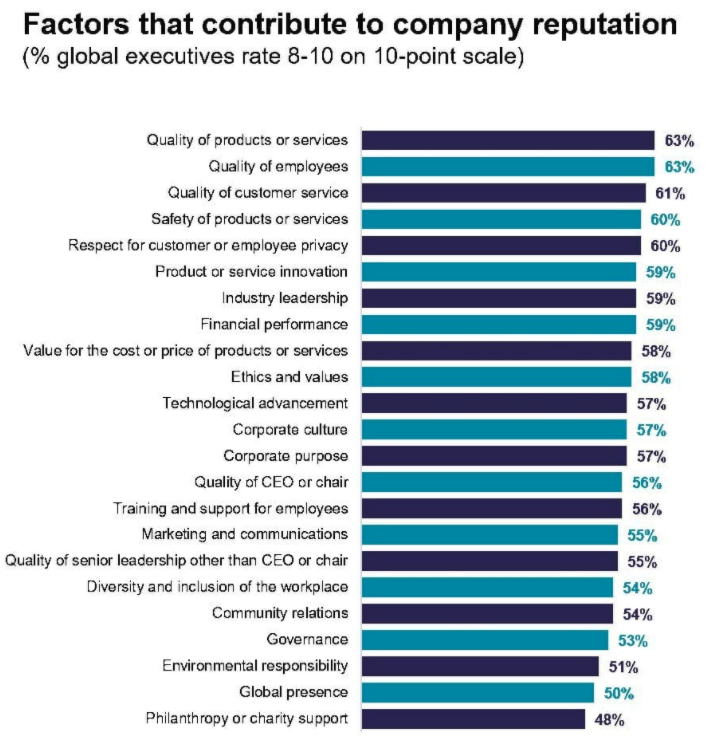
Is it important to monitor and measure corporate reputation?
These days, corporate reputation must be measured, and the results should be communicated to stakeholders to maximize the company’s market value.
As technology and innovation continue to move us forward in a global business market, it’s pivotal for business leaders to be prepared for anything that challenges their corporate reputation. The advent of social media and the growth of the internet across the globe have made reputations more accessible, assailable, and fragile because of how quickly negative information or misinformation can spread to the masses.
Corporate reputation management is as crucial as ever because the spotlight on corporations has never been brighter. One slip up and a mistake can go viral almost instantaneously.
Reputational opportunities and threats are around every corner, both internally and externally. For this reason, corporate executives must always be cognizant of their company’s reputation and willing to work to continuously maintain a positive image.
Many of the dangers that catch business leaders off guard when it comes to their company’s reputation are not hard to find. It’s just a matter of corporate leaders being aware of all factors when building and maintaining a company reputation.
Benefits of having a strong corporate reputation
Those business leaders that do manage and measure their corporate reputation, especially when they get some help with their reputation, often see major benefits. Executives across the globe ranked the top 12 advantages of having a strong company reputation.

How do you measure corporate reputation?
Measuring corporate reputation may seem amorphous, but it’s not. When asked how their company’s reputation gets measured, executives most often report factors such as employee satisfaction or engagement, sales and financial performance, and surveys among various stakeholder groups.
These are all great gauges of corporate reputation. However, there are a few go-to resources that can be used to measure a company’s reputation.
The Reputation Quotient
The reputation quotient model by Harris-Fombrun gauges stakeholder perception.
The model is a standardized and comprehensive corporate reputation measurement and something business leaders use to better understand the perceptions of corporate stakeholders such as consumers, investors, employees, and key influentials. It takes into account six dimensions and 20 attributes that are graded by research participants. When put on paper, the model looks something like this:
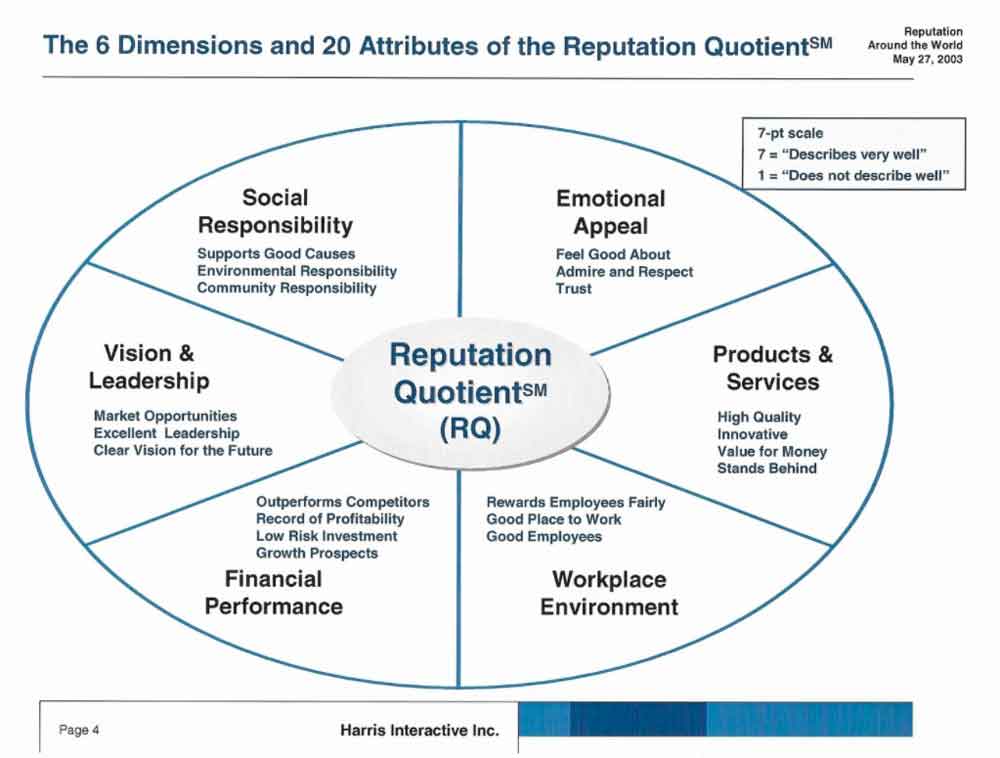
The reputation quotient model’s results are published annually in a report that has become known as The Harris Poll. A good ranking in the Harris Poll can significantly boost a company’s market value.
Viewed by most as empirical validity of corporate reputation, the reputation quotient is trusted by the masses and helps drive public perception. Since it began being used in 1999, the reputation quotient model has proven to be an invaluable tool for corporate leaders to use when managing their company’s reputation and identifying new market risks and opportunities.
Shareholder Value
It’s no secret that shareholder value can be a direct indicator of a company’s reputation. It makes sense that investors would be more likely to buy stock in a company with a good reputation rather than one with a bad reputation.
When an organization’s reputation is strong, a portion of its shares that investors buy can be attributed to that reputation. The percentage of a company’s market value that can be attributed to corporate reputation is called Reputation Contribution.
Here is how some of the world’s top-ranking companies looked in 2017 when it comes to Reputation Contribution, including the approximation of each company’s Reputation Value:
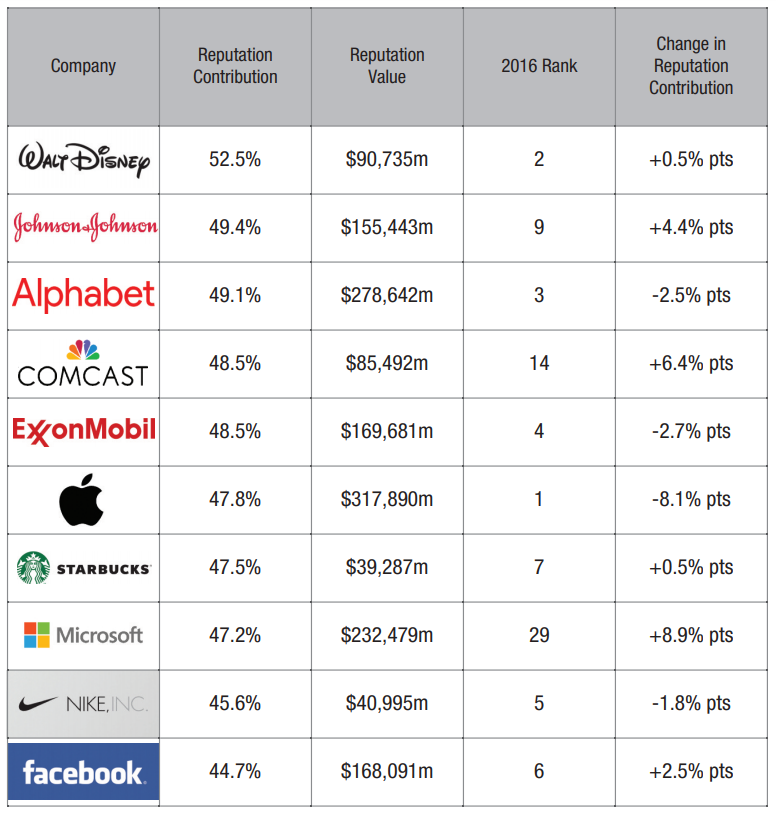
Measuring corporate reputation based on shareholder value can be related to many things, including:
- Public perception of your company
- Positive/negative press
- How likely investors are to buy shares
- How many shares are bought
- Company growth
All of the above can be affected by the way trusted financial entities such as Fortune report on your company. Shareholders trust the opinions of such publications and will be more likely to invest in a company that lands on the Fortune World’s Most Admired Companies list or similarly prestigious reputation lists.
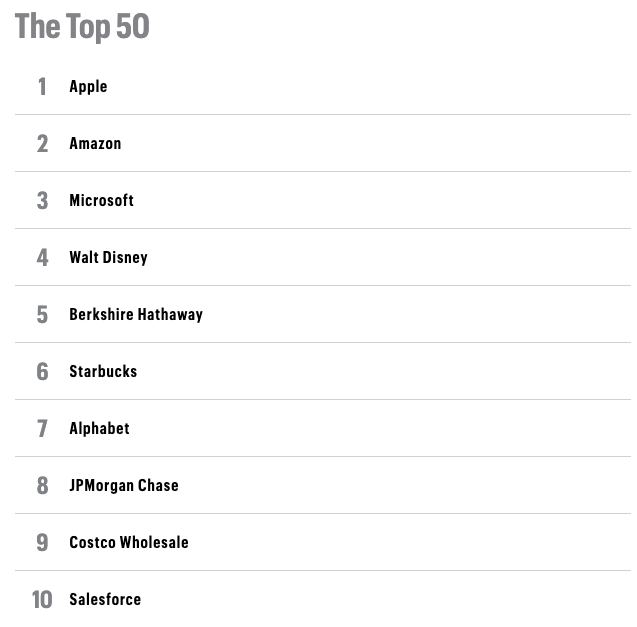
It should be no surprise that companies whose corporate reputations are so strong that they earn a spot as one of Fortune’s Most Admired Companies, such as Berkshire Hathaway and Amazon, also routinely show up on the list of highest-priced stocks.
Net Promoter Score
A company’s Net Promoter Score, or NPS, is a measurement of customer experience and a predictor of business growth. It is a proven and trusted method of gauging aspects of corporate reputation like customer satisfaction and public sentiment.
Using a 0-10 scale, customers are asked to rate how likely they would be to recommend a certain brand or company to a friend or colleague — 0 being not likely at all and 10 being extremely likely. Scores 0-6 establish a category of “Detractors,” 7-8 are considered “Passive” scores, and those that answer 9 or 10 are considered “Promoters” of that particular brand. True to its name, if you subtract the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters you get your Net Promoter Score. If every customer was a Detractor, your score would be -100%. If every customer is a Promoter, your score would be 100%.
How do you fix a damaged company reputation?
Now that we’ve touched on the factors that determine a corporate reputation and how to measure the value of a company’s reputation, let’s discuss what to do if you’re dealing with an already damaged reputation.
Each of the aforementioned measurements (and therefore a company’s overall reputation) can be improved when the company’s leaders take appropriate steps. It often takes some help from a trusted reputation management company.
Just as a company’s reputation is omnidriven, a reputation repair approach should typically be multi-pronged to maximize results.
Reputation management services such as review management, Wikipedia editing, and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) each can have a positive effect on corporate reputation, and they all are more powerful when combined. Running a reputation management campaign that encompasses all these services would improve your NPS, shareholder value, and reputation quotient by contributing to public sentiment.
When people need to find information about a company to help them form a first impression, what do they do? Perform a Google search, right? Combining all these reputation management services helps ensure they see positive content on the search engine results pages, thus contributing to a better corporate reputation.
Wikipedia and review platforms are among some of the highest-ranked websites in search results. When a company is searched, especially a well-known company, the search results often prominently display its Wikipedia page (if it has one) and review sites such as Yelp (or industry-specific review sites). Improving the content on these websites will only boost your overall corporate reputation. Basic SEO services can also help get any other positive content about your company to become more visible on the Internet.
Conclusion
It’s indisputable that corporate reputation has a major impact on market value and a company’s overall success. Business leaders need not only to be aware of the many factors that contribute to their company’s reputation, they also must know how to measure the value of their corporate reputation so that they do not get blindsided by a situation that could affect their bottom line. Measurements such as the Reputation Quotient, shareholder value, and the Net Promoter Score are good indicators of corporate reputation. If you find that your company’s reputation has already taken a hit, seek help from reputation management professionals that can help get you back on track.
FAQs
Q: How much is corporate reputation worth?
A: According to a recent report released by Weber Shandwick (in partnership with KRC Research) called “The State of Corporate Reputation in 2020: Everything Matters Now,” executives worldwide attribute an average of 63% of their company’s market value to their corporate reputation. That’s nearly two-thirds of a company’s market value being determined by how the company is perceived by stakeholders (i.e. customers, investors, employees, etc.).
Q: What factors influence a company’s reputation?
A: Everything matters. From work environment, to quality and safety of products and services, to corporate culture, to community engagement, and so forth. Some of the biggest factors on company reputation that global executives ranked include quality of products and services, quality of employees, quality of customer service, amongst many more.
Q: Is it important to monitor and measure corporate reputation?
A: Corporate reputation opportunities and threats are around every corner, both internally and externally. For this reason, corporate executives must always be cognizant of their company’s reputation and willing to work to continuously maintain a positive image. Many of the dangers that catch business leaders off guard when it comes to their company’s reputation are not hard to find. It’s just a matter of corporate leaders being aware of all factors when building and maintaining a company reputation.
Q: How do you measure corporate reputation?
A: When asked how their company’s reputation gets measured, executives most often report factors such as employee satisfaction or engagement, sales and financial performance, and surveys among various stakeholder groups. The Reputation Quotient, Net Promoter Score, and shareholder value are measurable gauges of corporate reputation.
Q: How do you fix a damaged company reputation?
A: Reputation management services such as review management, Wikipedia editing, and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) each can have a positive effect on corporate reputation, and they all are more powerful when combined. Running a reputation management campaign that encompasses all these services would improve your NPS, shareholder value, and reputation quotient by contributing to public sentiment.
“Significant coverage” addresses the topic directly and in detail, so that no original research is needed to extract the content. Significant coverage is more than a trivial mention, but it does not need to be the main topic of the source material.
About the author

Kent Campbell is the chief strategist for Reputation X, an award-winning reputation management agency based in California. Kent has over 15 years of experience with SEO reputation management, Wikipedia editing, review management, and strategy. Kent has helped celebrities, leaders, executives, and marketing professionals improve the way they are seen online. Kent writes about reputation, SEO, Wikipedia, and PR-related topics and is an expert witness for reputation-related legal matters. You can find Kent’s biography here.
–
