How to Measure Brand Reputation – Key Metrics, Tools, Analysis

Measuring The Impact of Brand Reputation
- Measuring the value of the reputation of a brand is important yet challenging.
- Brand reputation is only becoming more valuable.
- Measurement is difficult because reputation is an intangible asset. It is difficult to quantify how people think and feel about your brand.
- Key metrics that measure brand reputation involve online reviews, customer satisfaction, social media reach, sentiment analysis, and share of voice.
- Measuring customer loyalty using net promoter score, customer loyalty index, customer lifetime value, and/or repeat purchase rate.
- Measuring the value of brand reputation is accurately combining the impacts of quantitative vs. qualitative factors.
“A brand for a company is like a reputation for a person. You earn reputation by trying to do hard things well.”
Jeff Bezos
While there’s no singular method to quantify your brand’s reputation, there are metrics that make reputation management more effective. These metrics typically reflect consumer sentiment by tapping into customer reviews, online consumer behavior, customer loyalty.
For example, social media engagement metrics like likes, shares, comments, and follower count impact a brand’s online reputation score. 69% of job seekers are likely to reject a job offer from a company with a bad online reputation.
Table of contents:
Tools and Methods for Measuring Reputation
How to Implement a Reputation Measurement Strategy
Why Measure Reputation?
Importance for Businesses
Measuring reputation is high recommended for businesses as it significantly influences their success in the marketplace. A positive reputation not only attracts new customers but also drives customer loyalty and increases sales and revenue. Conversely, a negative reputation can lead to decreased sales and potentially irreversible damage.
Businesses that monitor and manage their reputation effectively can outperform competitors by fostering trust and reliability among consumers. Moreover, this translates into financial performance benefits like higher stock prices and return on investment.
“Reputation matters because it represents your point of view on the world and values. It’s why people come to trust you and it gives your media channel or brand credibility.”
Chris Lawson
Impact on Customer Trust
The perception of a brand plays a pivotal role in shaping consumer behavior, from purchase decisions to brand loyalty. As a result, a brand perceived as reputable and trustworthy can command premium prices and inspire customer loyalty. In turn, it is driven by the quality of the brand’s products or services and emotional attachment to the brand. Maintaining a positive reputation is essential for attracting and retaining top talent.
In fact, 83% of consumers reported trustworthiness being the emotional factor that’s most aligned with their favorite brands. In other words, brands seen as trustworthy engender more loyalty.
Preventing PR Crises
Proactive reputation management can prevent public relations disasters. By monitoring reputation metrics, companies can address potential threats swiftly, preventing minor issues from escalating into major crises. Effective crisis management involves having a comprehensive crisis plan and a trained response team to handle various scenarios. Thereby, they are protecting the company’s public image and minimizing the impact of negative incidents. Regular engagement with the community and stakeholders also builds a reservoir of goodwill, which can be very important during challenging times.
Key Reputation Metrics
Online Reviews
Online reviews and ratings serve as a direct reflection of a company’s reputation, influencing consumer decisions significantly. A high volume of positive reviews can attract new customers, whereas negative ones can deter potential buyers. Therefore, monitoring the quality and quantity of online reviews is thus essential for maintaining a favorable online reputation.
By keeping a close eye on key reputation metrics, companies like Reputation X can navigate the complexities of reputation management, ensuring a positive and robust brand image in the digital age.
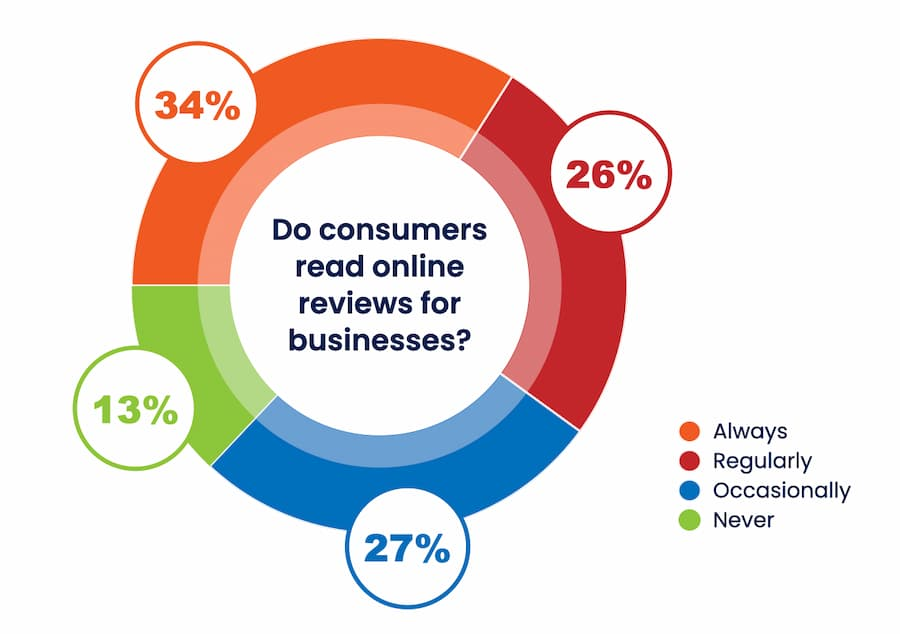
While 85 percent of consumers read online reviews for businesses, 92% are less likely to patronize businesses with negative reviews.
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction emerges as a pivotal metric, reflecting the extent of a customer’s happiness with a company’s products or services. This metric is important for gauging the overall fulfillment and contentment of customers, which directly impacts brand loyalty and advocacy. Companies typically measure customer satisfaction through surveys, feedback forms, and by analyzing both complaints and compliments. High levels of customer satisfaction can lead to a customer becoming a brand advocate, spreading positive word-of-mouth and influencing others to engage with the company’s products or service.
Social Media Reach
Social media reach is defined as the estimated amount of users that could have contact with a social media post. Additionally, it stands as one of the most significant metrics. It is based on the number of followers, fans, subscribers, connections, and visibility percentage. This metric is instrumental in tracking social media efforts, measuring performance, and understanding brand awareness on social media platforms.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis provides a deep dive into the overall attitude of consumers towards a brand as expressed in digital conversations. This analysis categorizes sentiments into either positive, neutral, or negative. In addition, it offers brands insights to understand their audience better, identify improvement areas, and manage issues proactively that might harm their reputation.
Share of Voice
Share of Voice (SOV) measures the visibility of a brand compared to competitors, indicating the authority and awareness a brand holds among users and potential customers. For that reason, it is a key metric to look at for understanding where a brand stands in the market, helping in making informed strategic decisions.
Tools and Methods for Measuring Reputation
Survey Tools
- Net promoter score (NPS): An annual NPS survey will tell you how likely customers are to recommend your company to others. Companies that have low NPS scores will likely see few repeat customers and experience negative impacts on their stock prices and financial statements.

- Customer loyalty index (CLI): Much like the NPS, a customer loyalty index (CLI) tells you the likelihood that someone will buy from you in the future, try your products or services, or recommend you to others. Insights from CLI surveys can guide you in adjusting your strategy to better meet the needs of your customers.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV): You can judge the loyalty of your customers without surveys or outside insights by basing it on their customer lifetime value. This is a simple calculation of your annual per-customer revenue, times the number of years they have been a customer, minus your original customer acquisition costs. Losing long-term customers or those with a high customer lifetime value can tell you that something isn’t quite right with your business.

- Repeat purchase rate: This is another metric that requires no outside surveys or information. You calculate your repeat purchase rate by dividing the number of repeat customers in a given one-year period by the total unique customers in that same annual period. If, year over year, you’re seeing a decrease in your repeat purchase rate, you likely have a degrading corporate reputation.
Qualitative vs. quantitative corporate reputation measurement
Over the years, many researchers have worked to create a formula for measuring corporation reputation value. Moreover, Any true measurement of the value of corporate reputation would have to include both quantitative and qualitative factors. Quantitative being things you can count, and qualitative factors are people’s feelings and perceptions about their experiences with your company.
The industry has yet to universally accept any single measurement tactic because no matter how you approach calculating the value of something intangible like reputation, it requires some quantitative measurement.
Here’s a look at some of the studies and measurement models researchers have created.
- Brand Equity Ten: David Aaker posited that there are ten brand attributes companies can use to analyze the strength of their company. His study cannot place a precise number on these different attributes, though, as they are qualitative measures, such as perceived value, brand awareness, brand personality, etc.
- Brand Equity Index: Bill Moran created the brand equity index using market share, relative price ratio, and durability of a brand. While the index is more quantitative, the measures are not always found to measure a brand’s value truly.
- BrandAsset Valuation: This index takes into account four areas of a brand to measure its value. Those areas include differentiation, relevance, esteem, and knowledge. Though very valuable, the measurement tactic is extremely qualitative.
Social Media Monitoring Tools
Social media monitoring tools are essential for tracking and analyzing online conversations and sentiment about a brand. Tools like Hootsuite and Sprout Social offer centralized dashboards where businesses can monitor mentions, hashtags, and direct messages across multiple platforms.
These tools provide the functionality to respond to interactions promptly, which is crucial for maintaining a positive online presence and managing potential PR crises. Additionally, platforms like Mention and Meltwater enable real-time monitoring of a wide range of online sources, enhancing the ability to manage a brand’s reputation effectively.
Analytics Platforms
Analytics platforms play a critical role in transforming qualitative data into quantifiable insights. Google Analytics, for example, offers detailed reports on website traffic and user behavior, which are vital for understanding the impact of online reputation on customer engagement].
Similarly, tools like Meltwater and Brandwatch provide media intelligence and social listening capabilities that allow businesses to track brand mentions and analyze sentiment across various media outlets. These insights are invaluable for businesses looking to make data-driven decisions to enhance their reputation management strategies.
How to Implement a Reputation Measurement Strategy
In order to effectively implement a reputation measurement strategy, businesses must navigate through a series of structured steps. This process involves setting clear objectives, selecting the appropriate tools, and engaging in both continuous monitoring and adjustment to ensure the strategy remains aligned with the brand’s goals.
Setting Objectives
The initial phase in developing a reputation measurement strategy requires businesses to define their objectives clearly. This involves determining the desired outcomes of reputation management efforts, such as increasing customer trust, improving online ratings, or addressing specific issues. Selecting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with these objectives is a fundamental step. Common KPIs include Net Promoter Scores (NPS), sentiment analysis results, and social media engagement metrics [49]. Establishing baseline metrics before implementing reputation management efforts provides a benchmark for assessing improvements, ensuring that progress can be accurately measured [49].
“It takes 20 years to build a reputation and five minutes to ruin it. If you think about that, you’ll do things differently.”
Warren Buffet
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Continuous monitoring of the brand’s reputation is essential for assessing the effectiveness of the implemented strategy. This involves tracking progress using analytics platforms to monitor website traffic, engagement, and conversions, as well as monitoring social media metrics and online reviews and ratings.
Equally important is to adjust strategies based on the insights gathered. If certain tactics or channels are not delivering the desired results, businesses may need to reconsider and modify their approach. This could involve reassessing content strategies for social media platforms or tweaking search engine optimization (SEO) strategies to improve visibility in search results.
Search engine rankings and visibility are vital for measuring online reputation. In fact, Around 95% of traffic goes to the first page of search results, which shapes people’s first impressions of a brand.
Implementing a reputation measurement strategy is an ongoing process that requires dedication and flexibility. Businesses like Reputation X must continuously assess and refine their strategies to respond to evolving trends and potential roadblocks, ensuring their reputation management efforts are effective and aligned with their overall business objectives.
FAQs
How is reputation measured?
Reputation can be gauged through tracking a variety of indicators, such as customer satisfaction levels, the sentiment of consumers, the frequency and quality of online reviews, the number of times the brand is mentioned, and the overall level of engagement with the brand.
What metric is used to evaluate brand reputation?
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a key metric for assessing brand reputation. It involves asking individuals how likely they are, on a scale from 0 to 10, to recommend the brand to others. Based on their responses, individuals are classified as Promoters (scores of 9-10), Passives (scores of 7-8), or Detractors (scores of 0-6). A higher NPS suggests a stronger level of brand advocacy.
What is corporate reputation?
Corporate reputation is how your customers, investors, and stakeholders view you in the marketplace. Stakeholders can include your employees, prospects, influencers, shareholders, and even competitors. Corporate reputation impacts your market value and long-term success. Minor changes in how your stakeholders view you will have a lasting impact on your success.
What factors are considered in calculating a reputation score?
When determining an online reputation score, factors such as the number of customer reviews, the brand’s social media presence, and the accuracy of the brand’s listings across various platforms should be considered. These elements collectively influence the perception of the brand’s reputation online.
About the author
Kent Campbell is the chief strategist for Reputation X, an award-winning reputation management agency based in the San Francisco Bay Area of California. Kent has over 15 years of experience with SEO reputation management, Wikipedia editing, review management, and strategy. Kent has helped celebrities, leaders, executives, and marketing professionals improve the way they are seen online. Kent writes about reputation, SEO, Wikipedia, and PR-related topics, and is an expert witness for reputation-related legal matters. You can find Kent’s biography here.
–
