The Fastest Ways to Remove Google Search Results: Ranked

When negative information appears in Google search results, it can be damaging to your image. But is there a way to remove this information from search results? Absolutely. This guide provides time-efficient methods, as well as access to free templates, to effectively remove personal Google search results, delete negative or misleading content from Google, and manage your online reputation.
Fastest Method: Contact the Author Directly
The quickest way to change search results is to make them completely disappear from the website on which the content is published. There are two ways to remove search results at the source:
- Via the person who originally posted it, or the person they work for
- From the webmaster who manages the site.
NOTE: Before you reach out to someone, ask yourself what their motivation might have been to create the negative content in the first place. If they intended to harm you, reaching out might be a very bad idea. We have seen cases where attorneys sent a cease and desist letter only to have it posted alongside the original negative content – making things worse.
This method can work well with bloggers who do not have a stake in damaging your reputation and who honestly made a mistake or have the empathy gene necessary for them to regret their post. However, it does not work well with journalists who arguably have a stake in writing inflammatory content because it drives clicks and ad revenue for them or their publication.
Here are free email templates to request that content be removed or edited.
Unfortunately, in most cases, journalists simply don’t have the incentive to take something down, even if what they wrote is ruining an innocent person’s life. They will often cite the First Amendment or “preservation of the public record” as a rationalization for destroying someone’s life with their work.
Contact the Editor to Ask for Removal
If the author does not remove the content, maybe their Editor will.
Again, we provide free templates for you to start with here. If they agree to delete the content from the website, Google will typically delete it from search results within a few days or weeks. However, reaching out to the webmaster might not always yield positive results. Therefore, as with contacting authors, it is important to consider the potential outcomes before making contact.
Case Study: How We Removed an Article from a News Site
A young man falsely accused of a crime could not get a job. This is how we fixed it.
Reputation X uses many methods to remove negative articles and other content from Google and other places online. One such case involved a young man who had been falsely accused of rape. A college student, he paid for school expenses by performing private strip shows. One night he was asked to do a birthday show for a few women. He did the show and went home. The next day he was falsely accused of rape.
You see, the boyfriend of one of the women was a police officer with a terrible temper who, apparently, didn’t like the idea of a Black man performing a lap dance with his girlfriend. When he found pictures, he exploded. He got his girlfriend to accuse the young man of a crime. The case was later dropped, but not after local newspapers ran his photo and his name as an accused criminal. The case was dropped, but the damage remained.
Reputation X contacted the news organization that had run the story. The author would not remove the article, but the Editor agreed after many communications. We explained the issue and provided proof and a written statement from the young man. The outcome? The article was removed. We then contacted Google and had the article removed from search results as well.
One month later, he got his dream job.
How to Contact the Webmaster to Delete Content
Every organization is different. Sometimes, there is an author, an editor, or a blogger, but there is almost always a Webmaster.
The Webmaster usually runs the technical aspects of the website. Getting content removed involves contacting the webmaster directly. You can find the owner of a web page using a Whois tool like Whois.net or DomainTools. If a website does not have domain privacy enabled, you can often find the owner’s name, address, and phone number. Some websites do not share this information publicly; they anonymize their contact information. In this case, you can try the Contact Us area of the website or even use LinkedIn to search for the name of the Webmaster and then use an email finder like Hunter.io to get their contact information.
If the Webmaster Won’t Remove It, Maybe They’ll Modify It
That’s not the only way to remove search results from Google. If the author or webmaster is unwilling to delete the page entirely, you can ask them to remove specific search phrases related to your company from the content. For example, if your company name is Acme Widgets, asking the Webmaster or author to remove the name of your company from the article will make it less likely to rank in Google or other search engines. The next time a search engine crawls the page, it will not find the search phrase and should, in time, demote and then remove the search result.
The NoIndex Method: Making a Web Page Invisible to Google
Another alternative is to ask the webmaster to add a NOINDEX tag to the header of the HTML on the page. This tag instructs search engines not to crawl the page any longer. The page is typically deleted automatically from search results within a few weeks.
Removing Content at the Host Level
A blogger writes in a blog, an author in a publication, and the website is run by the webmaster. But there is another place you may be able to go if you cannot get content removed using any of the above methods. The company hosting the website.
Companies like GoDaddy and others have their own Terms of Service. For example, GoDaddy removed the website Daily Stormer because it violated GoDaddy’s terms of service by publishing content that could incite violence. Granted, this method can only be used in certain specific cases.
Direct Removal from Google
If the webmaster or the author cannot be contacted, the next step is to remove search results from Google directly. This process, known as de-indexing, removes the page from the Google index. However, this is only possible in limited cases, for instance, if the content violates Google’s terms of service, for copyright violations, or includes certain types of personal info.
Here are the ways to have Google remove search results:
- Removal due to terms of service violation
- Results about you
- Right to be forgotten
- Digital Millennium Act for copyright violations
When Can You Remove Search Results Directly from Google?
Google removes content in the following situations:
- Identity theft or financial harm: If the content includes bank account and credit card numbers, signature images, or other information, that could lead to financial fraud or identity theft.
- Sexually explicit information: If sexually explicit information has been posted without consent.
- Legal grounds: If the content violates copyright laws or other legal regulations.
- “Right to be Forgotten”: Under European privacy laws, personal information will be removed if it breaches these rules.
- Copyright violations
- Using Google’s Results About You
Recently, Google made it a little easier to remove personal information called “Results About You“. With this tool, you may be able to get Google to delete your home addresses, emails, or personal phone numbers from search results.

According to Google, “When you’re searching on Google and find results about you that contain your phone number, home address, or email address, you’ll be able to quickly request their removal from Google Search — right as you find them. “
To get Google to remove personal information right in search results, click on the three dots next to the result. Find more information here.
Removal Using “Right to be Forgotten”
If you are an EU citizen or a citizen of a country that recognizes the Right to Be Forgotten, you may be in luck (Americans are not so lucky). Personal information will be removed from Google if it is in breach of European privacy laws, sometimes known as “Right to be Forgotten” laws, if your government ID number or bank account exists on the page, or if an image of a signature (handwritten).
This is what you often see on a Google results page if results have been removed under data protection laws:

Deletion of Content Using DMCA
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is legislation in the United States, enacted in 1998, designed to address copyright challenges. It criminalizes the production and dissemination of technology, devices, or services intended to circumvent digital rights management (DRM) that protect copyrighted works.
Furthermore, the DMCA heightens the penalties for copyright infringement on the internet. One of its most notable provisions is the “safe harbor” clause for online service providers like Google, which shields them from liability for their users’ potential copyright infringements, provided they promptly remove or block access to the alleged infringing content once notified by the copyright holder.
This has led to the widespread use of “DMCA takedown notices,” where content owners can request the removal of infringing content from websites and platforms. The image below shows the form you would use to make a copyright removal request with Google.
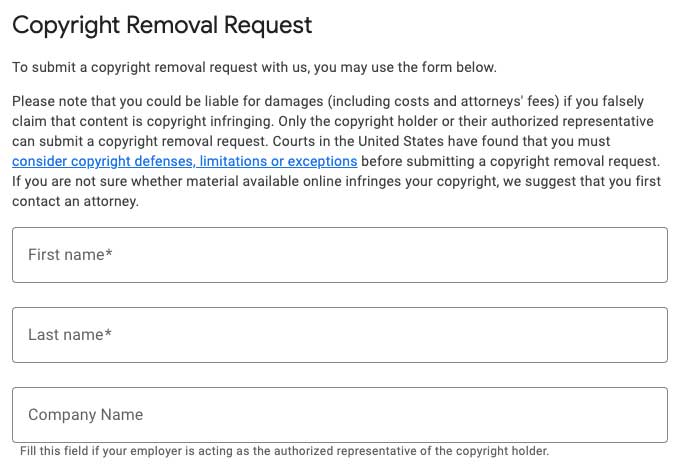
Want to give DMCA a try? Here is a link to the tool.
A Note About “Chilling Effects”
Google may (very often does) send a copy of each legal notice we receive to Chilling Effects for publication and annotation. This means that even though you have something deleted from Google search results, there will still be a notice at the bottom of the page that looks something like this:

When a searcher clicks on the notice, they may see a notice that shows the name of the person or entity that made the request to have the information taken down.

Chilling Effects reports DMCA, trademark, defamation court orders, private information, data protection, and government requests on its site.
Suppress (Push Down) Search Results
If the above methods don’t work, the next step is to suppress the search result so that it becomes less visible. Suppression campaigns work very often but take time. The upside is that they reduce the visibility of negative online content and replace it with positive content. When someone searches your name, they find only positive online content unless they really dig.
How Does Search Result Suppression Work?
Search result suppression effectively deletes Google results by making them difficult to find. Put another way, search results suppression pushes negative articles, posts, images, videos, and social media posts down so they are seen far less often, if at all.
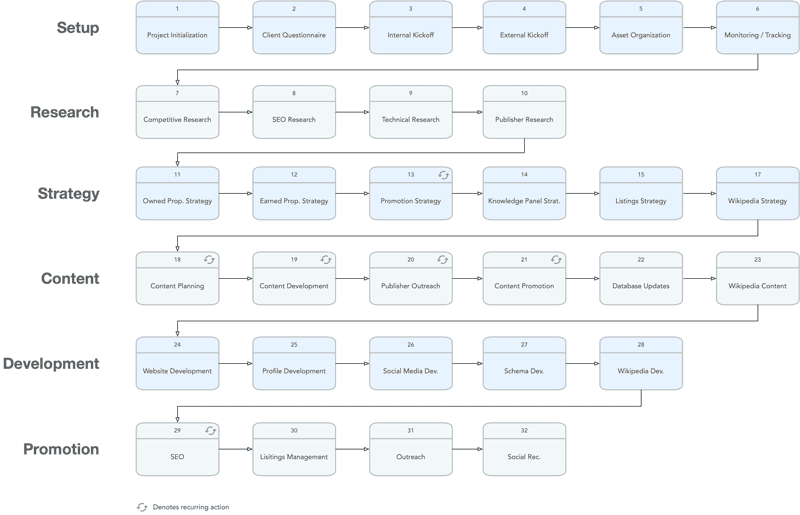
Search result suppression is the strategic process of reducing the visibility of specific damaging search results when certain keywords or phrases are used in search engines. The main objective is not to eliminate these results completely, which may often be challenging or impossible (see methods above). Instead, the focus is on pushing them down further in search results, where they are far less likely to be seen by users.
The term “push down” aptly describes the tactic used in this approach. Promoting positive or neutral content optimized for the same search terms makes it possible to have this preferred content rank higher in search results. As this content rises, the unwanted results organically get pushed down in the rankings, reducing the visibility of bad results.
While the ideal scenario would be to eliminate negative search results entirely, this is not always achievable. As a result, suppression becomes a more attainable goal.
The Legal Route
Should personal appeals or direct communication efforts to remove such content fail, considering legal counsel might be a good next step. It may be the most expensive way to get content removed as well. But if all of the other methods do not work, and you can afford it, the legal route may be worth a try.
When dealing with content that’s possibly libelous (meaning it constitutes written defamation), one strategy is to approach the legal team of the publishing entity. Most established organizations possess dedicated legal departments. But, it’s very important to furnish evidence that underscores the defamatory nature of the content.
Involving lawyers can streamline this process or increase your odds of success. If you need a recommendation for a defamation attorney, ask us. The act of a legal professional reaching out, particularly when their official letterhead tops the correspondence, can underscore the gravity of the situation. This alone can persuade parties to retract negative content, signaling seriousness on your part. Yet, engaging lawyers can be a lengthy process, and their services often come with a hefty price tag. Also, positive results aren’t always assured.
Lawyers versed in libel and defamation are adept at navigating the legal maze around erroneous and harmful content, be they in written (libel) or spoken (slander) form. They can argue for content removal or even go after damages if one’s reputation has demonstrably suffered.
Nevertheless, venturing down the legal route isn’t without challenges. Legal proceedings can be drawn out, necessitating many consultations, investigations, and maybe even court proceedings. While a lawyer’s expertise can strengthen your stance, it’s essential to compare the potential advantages against the costs. For many, the potential to restore a smeared reputation is worth the investment, especially when alternate methods have hit a dead end.
Conclusion
Maintaining a positive online reputation can be a matter of survival. While the process of removing negative content from Google may seem daunting, it’s entirely possible to use suppression, no indexing, legal methods, and others with the right approach and patience. Whether you contact the webmaster, request Google to remove the content, go the legal route, or opt for a suppression campaign, each method can help you regain control over your brand’s online image.
About the author
Kent Campbell is the chief strategist for Reputation X, an award-winning reputation management agency based in California. Kent has over 15 years of experience with SEO reputation management, Wikipedia editing, review management, and strategy. Kent has helped celebrities, leaders, executives, and marketing professionals improve the way they are seen online. Kent writes about reputation, SEO, Wikipedia, and PR-related topics and is an expert witness for reputation-related legal matters. You can find Kent’s biography here.
–
Tags: Business Reputation Repair, Individual Reputation Repair, Online Reputation Management Services, Online Reputation Repair.
