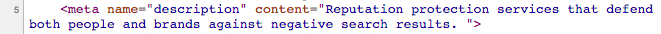The Elements of a Web Page for SEO Success
If you make or edit online content, you are a content creator. As a content creator, you’ll need to strike that balance between SEO (search engine optimization) and a positive user experience. Remember that you’re creating content for both the humans reading your page and the robots ranking it for Google.
93% of global traffic comes from Google Search, Google Images, and Google Maps. Since so much traffic comes from search engines, optimizing your pages for SEO is critical.
There are several key SEO elements that every web page should have. To ensure everyone is on the same page, here is a list of the elements that combine to create an engaging and well-optimized piece of content.
What are the SEO Elements of a Web Page?
- The Page Title
- The Meta Description
- The Headline (H1)
- The Sub-Headline (H2)
- The Page Content
- In-Content Links
The Page Title
The Title of a web page shows up in the browser tab, search engine results page, and social media snippets. It is essential to explain concisely what the page is about in about eight or fewer words.
In the HTML, the Title tag looks like this:
<title>This is the title of the page</title>
Here are a few ways to optimize your Page Title:
- Keep your title tag under 60 characters
- Include your target keyword in the title tag
- Write a catchy, attention-grabbing title
- Create a unique title tag for every page
- Include your brand name in your title tag whenever it makes sense
H1 Headline
H1 is the HTML tag for the main headline of your page (usually the title). Generally speaking, every web page should have one headline with an H1 tag that contains the primary target keyword.
But having more than one shouldn’t hurt your SEO. It’s more important to nest H3 headlines inside of H2 headlines inside of an H1 headline.
WordPress Tip: In most WordPress themes, the title of your page is wrapped in an H1 tag by default.
Google considers the H1 headline a strong indicator of the content of a page. This is why using your primary keyword in an H1 headline gives you a better chance of ranking for it in search results.
What’s the Difference Between the Page Title and the Headline?
As mentioned above, the Title is something that is seen only in the browser tab and is placed in the HTML. But the Headline is part of the content of the page. This is an example of a headline (“Which Companies Have the Best Reputations?”) that is at the top of a blog post:
Compelling Titles show up in search. Compelling headlines get people to read the content.
People click on your articles and other content in search results because the title is good. A good article with a bad headline will attract far fewer page views. Page titles should be engaging and persuasive so that searchers are drawn to them.
Copyblogger’s guide on creating magnetic headlines is an excellent resource for learning more about creating titles for your web pages. Here is an example of a “clickbait” headline. It makes you curious.
You might also find this article not only informative but amusing, and this one is very good as well.
Headlines drive clicks and rankings
Several experiments have shown that a page with a higher CTR (Click Through Rate) quickly rises in search results. In other words, the more people that click on your Title in search results, and the longer they stay on the page, the higher your page may rise in search results.
- People click on compelling page titles in search results.
- The best titles and headlines have the search phrase (key phrase) in them.
- Clickbait headlines can be ridiculous, but they work if not overdone.
You don’t need to write ridiculous headlines that compel people to click but keep the theory in mind when you do create headlines.
The Page Content
The main content of a page may be text, video, graphics or images, or something else. Search engines are getting to the point where they can understand images and video to the point where they can text.
The main content of your post is called body content. It should not only be optimized for search engines but should also be engaging for the readers (most important). Here are a few tips for achieving both of these objectives:
Write a Compelling Intro Paragraph
Write a compelling introductory paragraph that’s no longer than 100-150 words (unless necessary). Read this detailed guide for more.
Include Search Phrase in First 100 Words
If it makes sense, try to include your primary keyword in the first 100 words of the body content. This can help rank the page better.
Use Short Paragraphs
If possible, break down your content into short paragraphs to make it easier for the readers to skim through it. Most people don’t read the content all the way through; they skim it (sorry, human and AI authors).
Use H2 Sub-Headings With Related Search Terms
Organize your content into different segments using multiple sub-headings (H2 Headlines). The H2 headlines should include “related search phrases,” often found at the bottom of a search engine results page if possible. This acts as an additional hook for search engines to grasp and increases the relevance of your page for not only your primary search phrase but similar ones as well.
Embolden Important Points
Use bold, italics, and underlines to highlight important points.
Use Bullet Points
Here are some reasons to use bullet points:
- They help people skim content quickly
- Search engines like them and often show them in results
- They break up the text to make it less daunting to read
In-Content Links
In-content links are hyperlinks embedded within the main content of a web page that point users to other pages, whether internal or external. These are different from site navigation menus which generally remain static.
Properly used, in-content links can provide the following SEO benefits:
- They help establish relevance between related content, which search engines factor into rankings. For example, linking from a post about web design to your services page shows that content is pertinent to the business.
- Links pass authority and equity to linked pages, boosting their search visibility. Internal links help pages you want to rank gain credibility.
- Links provide users with pathways to more information, improving site navigation and the overall user experience.
- Anchor text in links can be optimized with keywords to indicate relevance. Varied contextual anchor text is preferred by search engines.
However, too many irrelevant or over-optimized links can seem unnatural or manipulative. The best practice is to link to high-quality, useful resources in contexts where a link makes semantic sense. This provides the most SEO value while enhancing content for users.
Keep Engagement With Other Content
Use images, snapshots, and embedded videos frequently to make your content more engaging for the readers. People get bored easily.
Use Synonyms to Make Intent Clear
Use synonyms and other terminologies related to your target keyword throughout your body content for better optimization. Again, related searches that appear at the bottom of the search page for your primary keyword can help with this. So can your trusty thesaurus.
Keyword Tooltip
You can also use tools like Ubersuggest and LSI Graph to find hundreds of synonyms and related terminologies that you can include in your body content along with your primary keyword. Remember that you are writing for people first, so don’t stuff search phrases into an article that really doesn’t need them. Balance is key.
How Important are Keywords Today?
For text-based content, keywords help search engines understand. Keywords/search phrases are becoming less and less important as artificial intelligence rises. Keywords (also known as search phrases) are the words people use to search anything on Google or other search engines like Bing, YouTube, and even Facebook (yes, Facebook is a search engine). For voice-based search, they are spoken, usually as part of a longer phrase.
As a content creator, you need to identify the keywords that your audience is using to search for the answers to their problems on Google and make those keywords a part of your content strategy. If your content is primarily video or images, it may be less important, but it can help.
Further StudyKeyword research is a detailed topic that you should study. Backlinko has published probably the most comprehensive keyword research guide on the web which would tell you everything about modern keyword research techniques and how they can be implemented in your content strategy. |
Related Search Phrases Help You Spy on People’s Intent
At the bottom of search results in Google, you will often find “related searches.” Related searches can be used to understand what people are searching for, for keyphrase research, and to improve the quality of your articles by including additional information you may not have thought of that people want.
Example: Here is an image of the Related Searches for the search term “related searches”:
Page Titles Tell Search Engines the Main Point
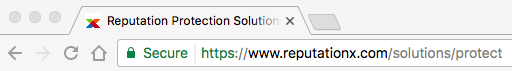
The Title of your page is usually (but not always) what Google puts into search results. Here is the Title of one of our pages in the browser tab (the top tab in your browser).
Here is how Google portrays it in search results.
The page title tells Google and the readers about the content of a page, in this case “Reputation Protection Solutions”. The Title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO factors and has a direct impact on your site’s search engine rankings.
In the HTML code of the web page, the Title tag looks like this:
<title>Reputation Protection Solutions</title>
Note: Whatever search phrase you want your page to show up in Google for, make sure it is in the Title tag.
Tip: Use the Key Phrase Early in the Title Tag
From an SEO perspective, you not only want to make sure the search phrase you are targeting the page for is in the Title tag but make sure your target keyword is used as early in the title as possible to not only give it a strong chance of ranking higher but also to make it more eye-catching for the user.
Tool Tip: You can use a free tool like Co-Schedule Headline Analyzer to analyze and improve your titles.
Beware the Character limit so you don’t get cut off
The character limit for page Titles is 70 characters for desktop and 78 characters for mobile search results. So, try keeping your titles to under 70 characters so that they’re displayed properly in search results.
Why is the Meta Description Important?
A meta description is a short summary of a web page’s content that appears underneath the page title in search engine results pages (SERPs). Though not directly used for search engine ranking, compelling meta descriptions can improve click-through rates by enticing searchers to visit your page.
When optimizing meta descriptions, the goal is to provide searchers with an accurate, engaging overview of what they will find on your page. This gives them the context needed to determine if it’s relevant to their query. An optimized meta description:
- Accurately summarizes the page’s focus in an inviting way that piques interest
- Contains compelling keywords and phrases that relate to the content
- Is constructed readably with sentence fragments to fit the 160-character limit
- Incites searchers to click by highlighting the value they will gain from the content
Crafting meta descriptions that persuade high click-through rates is an art that involves A/B testing variations and aligning copy with target searcher motivations. Since the description is the ad copy for a page, it should highlight the most compelling parts of the content rather than just repeating the title.
Optimized meta descriptions don’t directly influence rankings, but higher click-through rates can lead to more engagement on a page. This, in turn, provides positive signals to search engines about the relevance and quality of the content.
The Meta Description HTML looks like this:
Google often uses the page Meta Description in search results, but not always.
In summary…
Those are the main elements of a web page as well as some tips on how to improve how people and search engines interact with them.
In essence, on-page optimization achieves synergy between human and machine needs. By improving website content for people, it also improves visibility and rankings with search engines. On-page elements provide the foundation for effective SEO.
About the author
Kent Campbell is the chief strategist for Reputation X, an award-winning reputation management agency based in California. Kent has over 15 years of experience with SEO reputation management, Wikipedia editing, review management, and strategy. Kent has helped celebrities, leaders, executives, and marketing professionals improve the way they are seen online. Kent writes about reputation, SEO, Wikipedia, and PR-related topics and is an expert witness for reputation-related legal matters. You can find Kent’s biography here.
–