How Search Engines Work | From Archie to AI Search and Google
Brief Overview of the Role of Search Engines
You’re on the internet right now. You probably found this web page with a search engine. But have you thought about how search engines came to be the way they are today? The essential role they play is to organize the seemingly infinite amount of information available on the web and deliver the most relevant results to users’ queries. But there is a lot more to it.
What is a Search Engine?
At the most basic level, a search engine is a software program that is designed to search a database. That sounds pretty simple.
In the case of internet search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo, this database is a massive collection of web pages from around the globe.
When you type a query into a search engine, it sifts through snapshots of billions of pages to find matches – it does not instantly search the entire web. It then ranks these matches based on their relevance and quality. It’s a complex process that happens in fractions of a second.
We rely so heavily on search engines that they’ve almost become the arbiters of truth. Fixing search results through reputation management has become an industry once never imagined.
What Search Engines Are Good For
Search engines serve multiple roles beyond mere information retrieval. They’re a:
- Navigational tool: They direct users to specific websites or pages for which they’re searching. For instance, typing ‘Facebook’ in the search bar will lead you to Facebook’s official page.
- Informational tool: They provide users with knowledge and answers to their queries. For example, asking ‘Who is the president of the United States?’ will give you the Joe Bidens name.
- Transactional tool: They assist users in completing certain web-based transactions. For instance, you could search for ‘buy running shoes online,’ and you’ll get a list of online stores selling running shoes.
Early Search Engines
Archie
Archie, short for “archives,” has the distinction of being recognized as the first internet search engine, although its functionality was radically different from what we associate with modern search engines. Invented in 1990 by Alan Emtage, a student at McGill University in Montreal, Archie marked the beginning of search technology.
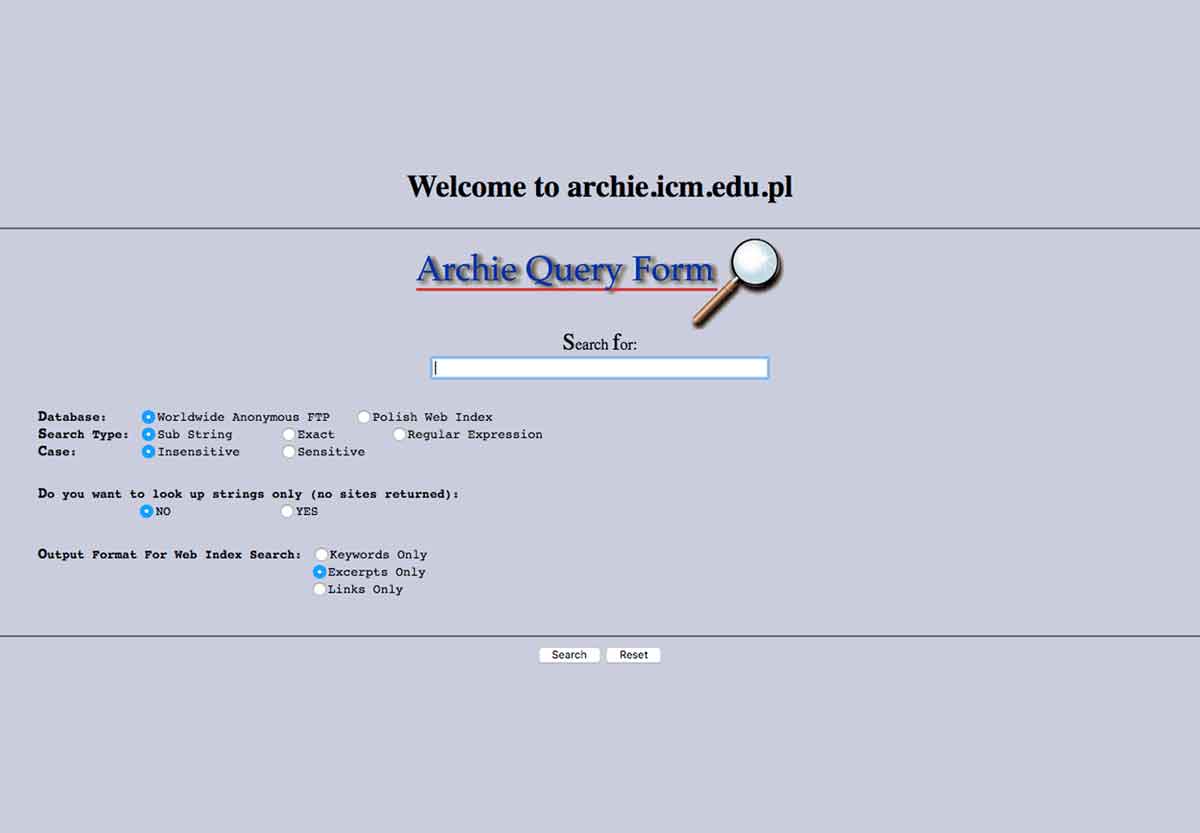
How Archie Worked
Archie used a script-based data gatherer to collect the directory listings of all the files located on public FTP servers in a given network of computers (on the Internet). The listings were then stored in a single database.
An FTP server is a computer server that uses the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) to store and share files. It allows users to upload, download, or even delete files from the server. FTP servers can be accessed remotely via FTP client software.
Users could access Archie and search for a specific file or browse the listings. Archie would then provide the FTP server address to the user, from where they could download the file.
While Archie didn’t search the contents of the files (as modern search engines do), it was a significant step in making the internet more usable. It essentially served as a giant directory of downloadable files.
Archie ceased operations in the late 90s, but there is an archival version preserved for historical reasons.
AltaVista
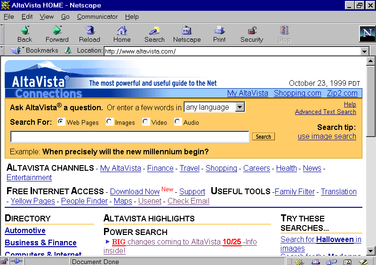
In the mid-1990s, an innovative new search engine emerged on the scene: AltaVista. Launched in 1995 by researchers at Digital Equipment Corporation, AltaVista significantly advanced the capabilities of search technology and is regarded as a pioneer in the field.
AltaVista was among the first search engines to index a significant portion of the web, boasting that it could store and retrieve all the words of every page it indexed, not just the file names or metadata. At its launch, it had indexed 20 million web pages, an astonishing number at that time. By comparison, other search engines of the era indexed only a fraction of the available web content.
Back in the day, search engine optimization during the initial years of AltaVista was far easier than it is today. It simply required a lot of cutting and pasting of original material to improve search results.
Directories: Yahoo
Yahoo, launched in 1994, started as a web directory, which is different from a search engine. Instead of using spiders to crawl the web, directories like Yahoo categorized websites into a hierarchical structure based on the subject matter.
The purpose was to organize the internet into a browsable format, like a digital directory or Yellow Pages. Yahoo’s staff manually reviewed and sorted websites into appropriate categories. This manual directory approach was useful when the web was still young, making Yahoo a dominant player in the early internet era, paving the way for more sophisticated search systems.
Manually Curated Lists of Websites
The original version of Yahoo worked like a giant, digital catalog of the web. It relied on human curation, with staff manually reviewing each website submission. These websites were then sorted and listed under various categories and subcategories based on their content. Users could browse through these categories or use a rudimentary search function to find sites listed under specific topics. This manual curation ensured a level of quality control but was excruciatingly labor-intensive and unable to keep pace with the rapidly expanding web.
Despite these limitations, Yahoo’s approach was revolutionary for its time.
Larry and Sergey’s Project at Stanford: Google
In 1996, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, then Stanford University Ph.D. students, embarked on a research project aiming to improve web search. Their novel approach was to rank pages based on their inbound links using an algorithm named “PageRank”.
The logic was simple yet revolutionary: a webpage is important if other pages link to it. This marked the birth of Google, which transformed the internet search paradigm by delivering more relevant results than ever before. Google’s innovative approach quickly outpaced its competitors.
Explanation of the PageRank Algorithm
Google’s distinctive feature was its PageRank algorithm, a revolutionary concept in search technology. PageRank evaluated the importance of web pages not merely based on their content, but also on the number and quality of links from other pages.
In essence, a link from one page to another was seen as a vote of confidence, indicative of the linked page’s value. The more high-quality links a page received, the higher its PageRank score, and the more likely it would appear in search results. This focus on link analysis allowed Google to provide more relevant and reliable search results, setting it apart from other search engines.
Link building is still a big part of SEO even today, although far less than it once was.
The Early Google Patent
The PageRank algorithm was such a game-changer that Google filed a patent titled “Method for node ranking in a linked database.” This patent, which was officially granted in 2001, detailed how Google used link analysis for ranking web pages. This approach was unique in the realm of search technology. It was this method of understanding and categorizing the internet, which was far more effective than previous systems, that played a crucial role in Google’s rise to dominance.
GOOG-411 and ChaCha
Search engines didn’t simply appear on mobile phones instantly. Early on, mobile rates were prohibitively high. So, real people were used. Between 2006 and 2010, text-based search services like GOOG-411 and ChaCha (242-242) provided solutions for finding local businesses and answering questions when mobile internet access was still a luxury.
GOOG-411, launched by Google in 2007, allowed users to call a toll-free number and use voice commands to search for local business information. The service ceased operations on November 12, 2010. ChaCha, on the other hand, was a text-based service launched in 2006, where users could send queries to 242-242 and receive answers from human operators. ChaCha also ceased operations in 2010.
These services were quite valuable during a time when accessing the internet on mobile phones was both expensive and limited. They helped bridge the gap between traditional directory assistance and the more sophisticated search engines that dominate the market today. As smartphones became more prevalent and affordable data plans became the norm, the demand for such services declined, marking the end of a brief era in the evolution of search.
Modern Search Engines
Today, Google, Bing, and Baidu represent the forefront of search technology, each with unique characteristics.
- Google, with its sophisticated algorithms, delivers highly relevant results and provides an array of specialized search features.
- Bing, Microsoft’s offering, is integrated with many Microsoft products and provides unique features such as Video homepage and Image search.
- Baidu, the leading search engine in China, is tailored to the Chinese language and offers services deeply integrated with Chinese culture and regulations.
Each of these search engines has carved out its niche, serving different user needs and preferences.
Differences Between Early and Modern Search Engines
The transformation from early search engines to modern ones represents a significant evolution in speed, accuracy, and personalization.
Speed: Early search engines were way slower, taking longer to index the web and return search results due to technological limitations. Modern search engines can scan the caches of billions of pages within fractions of a second, delivering instant results. Notice the word “cache”. One of the things that makes search engines fast is that they aren’t actually searching the web in real-time, just a snapshot of it.
Accuracy: Initial search tools, like Archie, only indexed file names on FTP servers. Modern search engines analyze the full content of a webpage, including text, images, and links, leading to more precise results. Google’s PageRank algorithm revolutionized accuracy by considering the quality and quantity of a page’s inbound links.
Personalization: Early search engines provided the same results to all users. Today, search engines like Google tailor results to individual users based on their search history, location, and other personal data, enhancing the relevance and usefulness of search results. This level of personalization was unfathomable in the early days of search technology.
Elements of a Modern Google Search Result
Modern Google search results are not just simple lists of links. They’re now rich, structured presentations that blend various elements, providing users with a comprehensive experience. Let’s explore the key elements of a modern Google search result.
AutoSuggest and AutoComplete: Helping Users Formulate Queries
When you start typing a search query into Google, you’ll notice a dropdown list offering suggestions for what you might be looking for. This feature is called AutoSuggest. It helps by proposing queries based on what other users have searched for and what is trending. Autosuggest is a prediction of what you may type.
AutoComplete is different, it tries to predict and complete your query as you type. These features are invaluable for users who may be unsure of how to phrase their search or are looking for quick results.
AutoSuggest queries are based on:
- Trending topics
- Popularity of the search
- Search history
- User location
- User language
Google uses RankBrain (2015) to understand user intent of a search query. It’s an understanding algorithm that connects the meaning between words.
Image Carousels: Visual Search Results
In some search results, you might notice a horizontally scrolling list of images at the top of the page, known as an Image Carousel. They look like this:
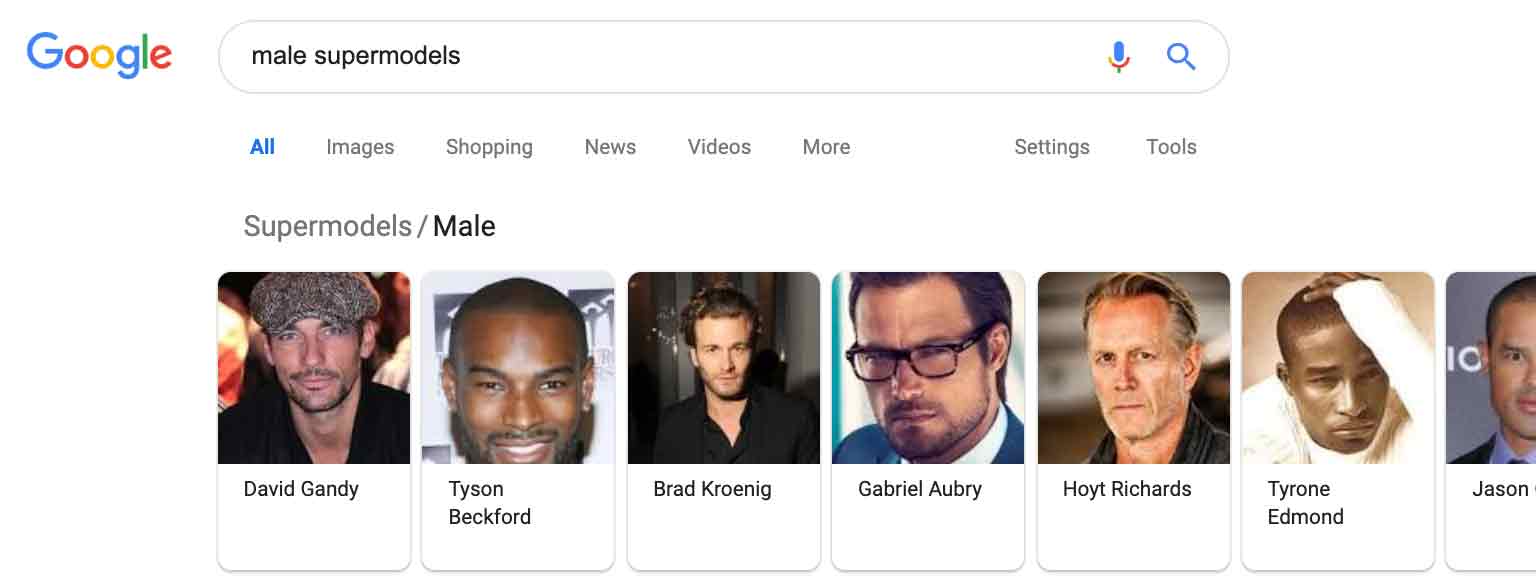
This feature is particularly useful for visually oriented searches, such as when looking for products, recipes, or places. By providing a visual representation of the content, Image Carousels allow users to quickly assess the relevance of the results before clicking through to a particular page.
People Also Ask: User Queries in Depth
Another much-used feature is the People Also Ask (PAA) box, which provides a list of questions related to your search query, along with short answers. When you click on a question, it expands to display a brief answer and a link to the source. PAA boxes are especially helpful for users seeking more in-depth information on a topic, as they often provide different angles or related aspects that the user might not have initially considered.
Note: “People Also Ask” is different from “People Also Search For“.
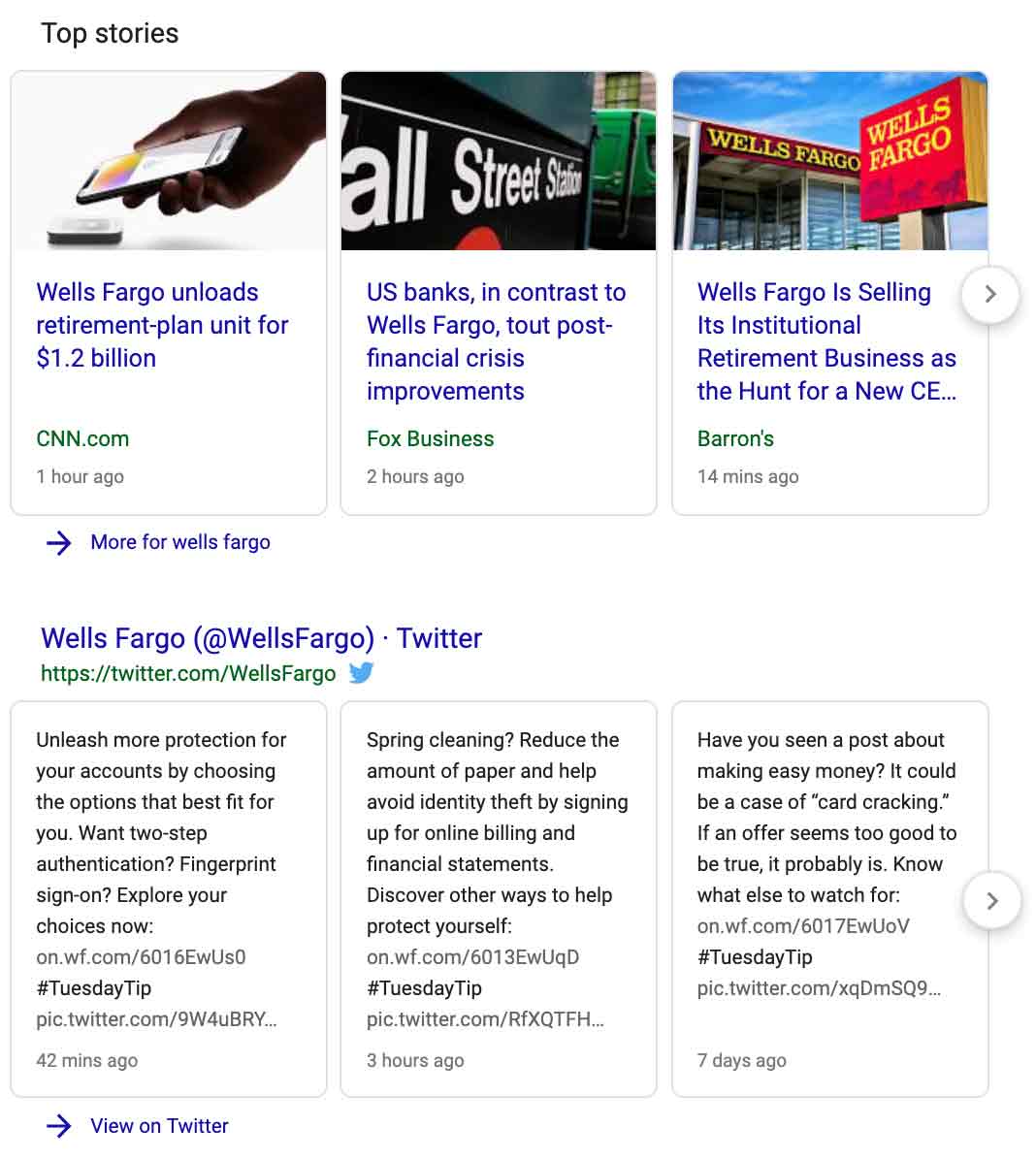
Top stories
When the entity being searched generates enough news coverage a top stories section will appear at the top of the SERP. The top stories are pulled directly from the News tab and are mainly sourced from credible news sites.
Knowledge Panels
Knowledge Panels appear on the right side of the search results and offer a wealth of information on a specific topic, such as a notable person, place, organization, or event. They look like this:
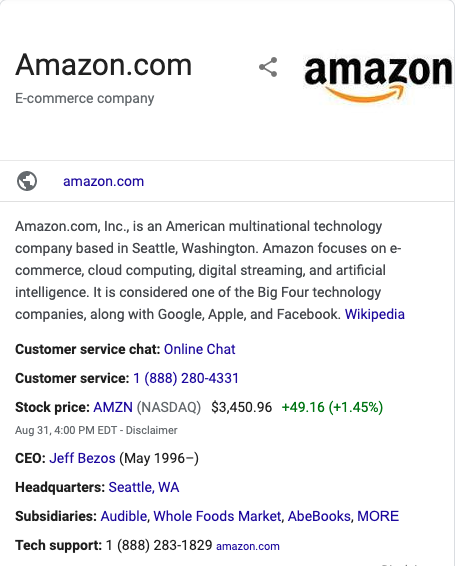
These panels are generated automatically and gather information from various sources such as Wikipedia to provide a summary, images, and pertinent data, such as birthdates or addresses. Knowledge Panels are particularly useful for users who are looking for a quick overview or specific piece of information on a topic.
Sitelinks
Sitelinks are additional sub-listings that appear underneath the first Google search result, usually for recognizable brands and organizations. These links provide a quick way for people to jump to the correct page on a website. The maximum allotted number of site links is six. The number of site links any search result gets depends on how well-structured the site is, and how much unique content it has. Want to know more about site links – this is a good resource.
Rich Snippets
Then there are rich snippets. Rich snippets provide additional information, such as a photo or a star rating. Since rich snippets are more visually pleasing and offer a better jumping-off point, they often have higher click-through rates. Brands can increase their chances of getting a rich snippet by adding structured data to a website. A rich snippet looks like this:

Other Elements: Ads, Maps, Local Packs, etc.
Google search results also include several other elements designed to enhance the user experience:
- Ads: Often appearing at the top of search results, ads are clearly marked and are relevant to your search query. These are paid placements by advertisers.
- Maps: For location-based queries, a small map may appear, showing relevant locations in your vicinity.
- Local Packs: Often accompanied by maps, local packs display information on local businesses, including reviews, addresses, and hours of operation.
The Role of AI in Search
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly reshaped the search engine landscape in breathtaking ways. Frankly, people are starting to freak out a little bit. The advent of ChatGPT in late 2022 caused Google to rethink its entire search engine. But before that, there were other important AI-related breakthroughs.
Google’s RankBrain, for example, is an AI-based component of Google’s search algorithm. It employs machine learning to understand the context and intent behind a user’s query, even if the phrasing is ambiguous or hasn’t been used before.
AI also powers personalized search, offering results based on individual users’ past behaviors, preferences, and locations. This tailoring provides a unique search experience for every user, making the results more relevant and useful.
AI supports voice search and natural language processing. With the rise of virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa, search queries are increasingly voice-based. AI helps interpret these spoken queries, understand the context, and provide accurate results.
AI has a substantial role in image and video search, improving the accuracy of visual search results by understanding the content within images and videos.
AI has evolved to become a cornerstone of modern search technology, facilitating a more intuitive, accurate, and personalized search experience. Its influence is set to grow as technology advances, offering exciting potential for the future of search.
The Future of Search: Predictive Search, Voice Search, and More AI
The future of search is already unfolding before us, with predictive search, voice search, and the continued integration of AI like ChatGPT and Googles Bard shaping the landscape.
Predictive search, also known as proactive search, aims to anticipate the user’s information needs before they even conduct a search. Google Discover is an example of this, recommending content based on a user’s browsing history, interactions, and location. As AI and data collection techniques become more advanced, we can expect predictive search to become increasingly accurate and personalized.
Voice search has been on the rise, thanks to the proliferation of voice-activated assistants like Google Assistant, Alexa, and Siri. With improvements in natural language processing and understanding, voice search is expected to become more sophisticated, understanding complex queries and engaging in more natural, conversational interactions.
Continued AI integration is set to further revolutionize the search landscape, aggressively. Google is even changing its search engine in significant ways by adding Bard results to the top of search results and moving traditional blue links further down on the search results page.
In essence, the future of search is geared towards creating a more intuitive, predictive, and personalized experience for users, offering precise information at the right time without the need for explicit queries. As technology advances, this future is rapidly becoming a reality.
About the author
Kent Campbell is the chief strategist for Reputation X, an award-winning online reputation management agency. He has over 15 years of experience with SEO, Wikipedia editing, review management, and online reputation strategy. Kent has helped celebrities, leaders, executives, and marketing professionals improve the way they are seen online. Kent writes about reputation, SEO, Wikipedia, and PR-related topics.
–
Tags: Knowledge Panel, Reputation Management.
