How to Delete Something from the Internet Permanently

The internet never forgets.
Once something is posted online, it can be challenging to remove it completely. This is especially true for personal information you may regret publicly sharing.
In this article, we’ll explore some methods for trying to delete your personal information from the internet, specifically from search engine results.
While not foolproof, there are steps you can take to make certain content less visible and accessible.
We’ll cover how to remove your name and personal details from Google search results, as well as requesting content removal from source websites.
Specifically, we’ll discuss:
- Using Google’s removal policies to submit takedown requests for search results that expose your personal information
- Contacting websites directly and requesting they remove pages or content related to you
- Taking advantage of your “right to be forgotten” within the European Union
Best practices for trying to limit your online footprint and exposure moving forward
While deleting something from the internet is challenging, this article will provide actionable tips that may help. With persistence and the right approach, you may be able to regain some control over your name and reputation online.
Eight Ways to Remove Google Results
How do you get something removed from a Google search? There are eight ways that do not involve a defamation lawsuit.
There are eight ways to remove content from search results:
- Results about you
- Ask people to delete their content
- Remove content at the publisher level
- Ask people to change their content
- Make a page invisible to Google
- Google removal request
- Suppress visibility
- Removing negative reviews
1. Use Results About You
The first place to go to remove content from Google search for personal information is Google’s “Results About You” feature. It is a tool for managing personal information that appears in search results.
Results About You works like this: If you find your contact details, like your email, phone number, or home address, in a search result, select “Remove result” from the menu icon next to the result.
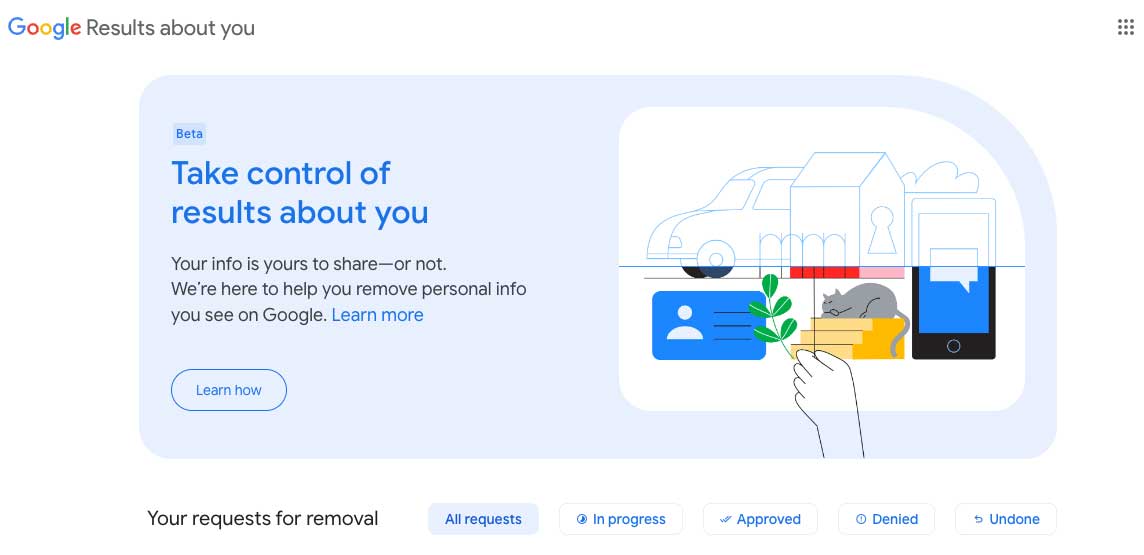
A detailed removal request form can be submitted for personal information that doesn’t include contact details or for illegal information like copyright infringement. Google will then review your request to make sure it complies with their policies. The process usually takes a few days.
Of course, removing a result from Google Search doesn’t completely delete it from the internet. Just because something has disappeared from Google results doesn’t mean it isn’t still accessible on the original website.
Read on for cases where the content that needs to be removed isn’t personal information.
2. Ask the Author to Delete It
First, the bad news. In our 15+ years of experience, we’ve found that a Webmaster will often not remove online content because, well, they posted it themselves. Perhaps it’s just human pride.
However, sometimes they will remove it. Either way, it’s worth asking. It often comes down to understanding what motivates them.
Use incentives to have content removed
We’ve made some interesting offers to our clients to get them to remove online content. Here are some examples:
- We’ve anonymously donated to charities.
- We’ve provided direct payment to the author.
- We’ve paid the site owner to take something down.
- We’ve shown them the error of their ways. For example, someone accused but found not guilty can sometimes have proof of innocence, and reputable publishers may take it down.
People are motivated by many things. You might be surprised by what works.
Customize your approach to asking for content removal
Every author who may have published something negative online is different. Conducting some research can go a long way in finding out what motivates someone and what is most likely to convince them to consider your request.
Note: It’s usually easier to work with individuals rather than companies – companies have lawyers, and lawyers are often conservative in their removal request views.
Now that you’ve thought about it – if you feel contacting the author to get online content deleted is the right approach, here are a few ways to persuade people to take down a blog post, article, video, or other online content.
Motivating someone to act
- Appeal to their altruistic side: “You had every right to post that review. I hope I’ve made it right. At this point, the post is really damaging my business – would you mind removing or updating it?”
- Try the charity angle: “I see you support the local little league. I know removing the post you wrote might take some of your valuable time. I’d be happy to donate to the _____________ little league in your name or anonymously as a thank you for taking it down.”
- Take the capitalist route: “I’d like to sponsor the page you wrote about our business. We’ll request a few modifications, and you’ll be well compensated for your time.” Note: Modifications may mean removing the business’s name, adding a special meta tag to make Google ignore the page (noindex), or removing the page altogether.
Note: Asking someone to remove content can have downsides
Reputation X works with attorneys who have made the sometimes huge error of sending a legal demand letter to a webmaster only to have the information added to the original page. Then, people comment on the newly refreshed content. Google often responds by making negative content rise in search results.
Email is convenient, but voices communicate better
A phone call is usually a better method of communicating with someone for the following reasons:
- It’s better the request comes from a human rather than an email. The human voice can communicate emotion far more nuancedly than written methods. If you have a true story of how the post is affecting you, a phone call is the way to go – if you can.
- Here’s another reason to use a phone call if you can: A voice conversation can’t be copied and pasted onto the internet directly. If a person wants to do you harm, the last thing you want to do is give them an easy way to copy and paste your plea onto the internet.
Free email templates to request removal
Here is a link to various templates to ask an author, editor, or Webmaster to eliminate content. They range from empathetic to strongly worded. Edit them as you see fit. You can find the content removal email templates here.
Why search results rise in search results when refreshed
Search engines like fresh content because it is seen as more relevant and timely. This is true for all online content, but the impact of freshness depends on the type of content it is. The news content must be very fresh – it’s news, after all – and, by its nature, has a limited shelf life. Blog content is less so, but it’s still important. If you want to learn more about the algorithm, check out this post.
You may often not want to contact the author because they may use your appeal to create more contact about your brand – making things worse. So, think before asking someone to remove content. You don’t want to make things worse.
3. Ask the Publisher to Remove the Content
If the author won’t remove the content, or you think it is a bad idea even to ask, consider asking the webmaster or publisher of the site upon which the information lives to remove the page completely.
This doesn’t often work on personal blogs because the webmaster, publisher, editor, and author are often all the same person. However, it can work on medium-sized sites like local or small-town news sites. In this case, the person to ask might not be the same person who wrote it. It might be their Editor.
How to find who owns a website to ask for a removal
To find the owner of a site, use a Whois tool like Whois.net or DomainTools. A little research can point you to someone in charge. But sometimes, that information is protected by domain privacy. If a website does not have domain privacy enabled, the name, address, and phone number of the owner of a website will often be visible.
You can also check the website’s Contact Us page or look up employees of the company that owns the site using LinkedIn.com.
When you find the right person, try modified versions of the steps outlined in the tactics to get online content removed section above.
Notice that no lawyers have been called yet. 🙂
4. If Authors Don’t Remove Content, They May Change It
In a case where the author refuses to remove the content from their websites, they may be willing to edit the content. In this case, ask the webmaster of the site containing the information to remove the search phrases from the page.
Remove the search phrase from the page
For example, if your company name is mentioned on the page or the description of the page (in the HTML) and the Title of the page (also HTML), the webmaster can change the words so your company name no longer exists on the page.
Here is an example of the “change keywords” tactic:
Let’s say you own a company called “Enron.” And a local publisher wrote a story with the headline “Enron CEO Caught Juggling Kittens.” You’d ask the publisher to change the headline to something like “Local CEO Caught Juggling Kittens.”
The article’s author would edit it to remove all mentions of the company, but the article would remain. Google would almost certainly drop the page visibility in search results. Why? Because the search phrase mentioning your brand is now gone.
The page may become less visible but not disappear from search results
The web page may not completely disappear because links from other pages may still mention the search phrase when they link to your site (the text in a link is called the “anchor text”), but the page would no longer be as relevant to search engines and would lose visibility. That means a drop in search results and reduced visibility when someone searches for your brand online.
This can work if the article has been up for quite some time and is no longer generating traffic and income for the publisher. Small publishers sometimes make this sort of change in return for compensation or out of the goodness of their hearts.
Spoiler alert: In our experience, editors rarely act from the goodness of their hearts.
5. Make a Page Invisible to Google Using NOINDEX
A web page doesn’t need to be deleted to disappear from Google. It is possible to ask the publisher to add a NOINDEX tag to the header of the HTML on the page. Unless they are at least a little bit technical, they’ll probably need to have their webmaster add the tag to the offending web page.
It takes about a minute to insert code to make a page disappear from Google
It can take a webmaster as little as one minute to add a NoIndex tag to a web page. Time isn’t the problem; it’s motivating the people in power to make the call, and that is the issue.
The article will remain but will drop from the search results
The good news for the publisher is that the article remains. But, Google ignores the article and drops it from search results. So will other search engines like Bing. Your company name still exists on the page, but the NOINDEX tag tells search engines not to crawl the page anymore. The page is normally removed automatically from search results within a few weeks.
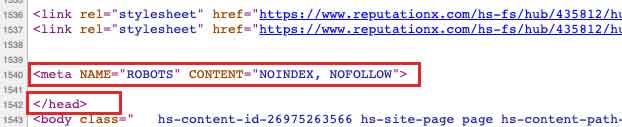
This is what a NOINDEX tag looks like:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Where does the NOINDEX tag go?
Whoever is placing the tag should put the NOINDEX tag inside the HEAD code in your HTML. The HEAD code is located at the top of the web page HTML code.
In the example below, we placed the NOINDEX (and NOFOLLOW) code just above the closing statement of the HEAD. The HEAD content is everything between these two tags in the HTML: <HEAD> and </HEAD>.
6. The Google Removal Request
This is different than Results About You. A search engine will remove information from search results in special cases. Here are some examples:
Identify theft or financial harm as grounds for removal
Reputation X has gotten many pages removed due to violations of terms of service. This month alone, we’ve gotten more than a dozen pages removed for this reason. Google describes the information they will remove, such as bank accounts, credit card numbers, signature images, or other information that could cause financial fraud or identity theft.
Google may remove something if the site charges for the removal (exploitive)
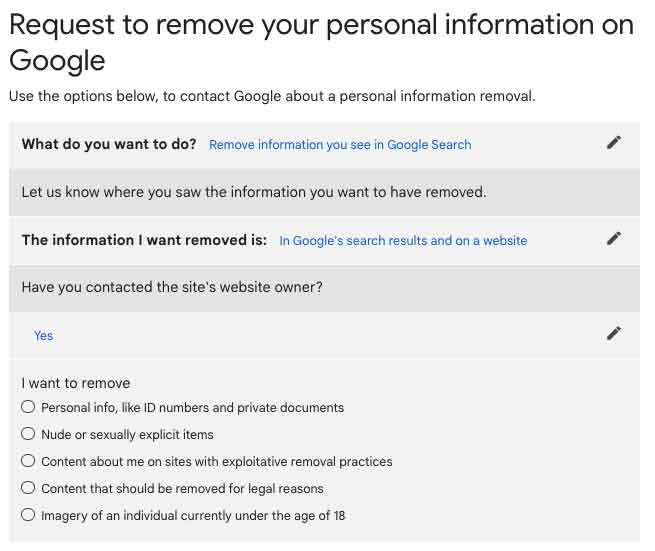
If a website has posted something negative about you and requires a fee to remove the content, Google may remove it from their search engine for you.
This does not apply to business review sites. This method does not remove the post. It only removes the post from search results. Here is the form for you to use. When you use it, make sure you select “exploitive removal practices.” This is what the form should look like when it is almost completely filled out:
Sexually explicit information can often be removed from search results
Sexually explicit information posted without consent will be removed from Google’s index. To qualify, it has to meet these criteria:
- You’re nude or shown in a sexual act without consent
- You’re underage
- You intended the content to be private, and the imagery was made publicly available without your consent (e.g., “revenge porn”)
- You didn’t consent to the act, and the imagery was made publicly available without your consent
Legal reasons search engines may remove content
Google and Bing will also remove copyrighted information. This falls under the “legal removals” area. It’s considered a “DMCA” removal. Google will ask which service you’d like information removed from, for example, Google web search, Blogger, YouTube, etc.
Types of content that may be removed include:
- Sites with malware or phishing software
- Trademark violations
- Certain kinds of personal information, like social security numbers
Europeans get the “Right to Be Forgotten,” but most others don’t
Personal information will be removed from Google if a web page breaches European privacy laws, sometimes known as “Right to be Forgotten” laws; if your government ID number or bank account exists on the page; or if there’s a hand-written image of your signature.
For copyright infringement, learn about the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA)
The DMCA protects copyright owners. Google often respects this, and they have a removal process for doing so. But we’ve found that using legal means works far more often than a simple DMCA take-down request on their site.
So, yes, lawyers do have a reason to exist (they’re some of our best clients)!
The downside of a DMCA removal
Google may send a copy of each legal notice they receive to Lumen (formerly Chilling Effects) for publication and annotation.
This means that even though you have something removed from Google’s search results, there will still be a notice at the bottom of the search results page saying something has been removed.
When a searcher clicks on the notice, they may see a notice showing the name of the person or entity requesting the information taken down.
7. Push Bad Content Down and Good Content Up: Suppression.
If none of the above methods will work, or if you think some may not be a good idea, there are still ways to clean up your search results. In this case, take a proactive approach and push harmful content down in search results by creating positive content to rise to the top.
How does suppression of online content work?
Secret: Suppression isn’t so much suppression as it is promotion. Suppression reduces the visibility of negative online content. Here is the logic behind the suppression of negative search results:
- Bing and Google want users to find the content displayed in their search engines valuable.
- To do this, they work to return the best possible search results.
- The best search results most appropriately fit the searchers’ intent – this is called “relevance.”
- By developing better content and promoting it properly, search engines treat the new content better than the old negative content.
- Better crafted, more relevant content promoted properly will often rise above negative content in search results.
Suppression, or pushing down negative search results, is the act of creating better content and promoting it to drive negatives down. Suppression is a viable alternative if information cannot be removed at the source or search engine level.
How do we suppress negative search results?
At Reputation X, we measure the strength of a given page based on an authority score – a number on a scale of one to one hundred. If the page to be buried has a high score, content must be created and promoted with a higher score. The higher the authority score, the more resources are needed to affect change. We select and create the right online content, then link it together using SEO best practices meant to stand the test of time.
That’s why our results tend to stick when the efforts of other reputation companies fail.
Click here to read about suppression services
8. Special Case: Removing Negative Reviews
Can Google reviews be removed? Yes, Google does remove reviews sometimes. To check if a review violates Google’s guidelines, check this page.
Violation of terms of service of the review site
Reviews can be removed if they violate the review site’s terms of service (TOS). Yelp will remove certain types of comments and bad reviews, which will, in turn, increase your star rating. Check Yelp’s content guidelines to see if the review violates any of them and flag it.
Be patient when removing reviews
Sometimes, it takes months to get reviews removed. Some of the most common review content that warrants removal includes:
- Threats
- Harassment
- Inappropriate content
- Spam or fake content
- Off-topic content
- Illegal content
- Sexually explicit content
- Conflicts of interest
Statistics About Damaging Content
65% of people trust search engines for research. When something negative appears in search results like Google or Bing, most people and businesses want to know how to remove it.
Here are some interesting statistics on search results and reviews:
- Only 5% of people look past Google’s first page (10 positions).
- 85% of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations.
- 60% of consumers say negative reviews made them not want to use a business.
- 49% of consumers need at least a four-star rating before using a business.
- Most people will not do business with a company once they read a single negative review. Ouch.
What people see online about a brand, whether personal brand, company products, or services, can make or break opportunities.
Whether search results are true or not is less important – people tend to believe search results either way.
Can Google remove information from a website?
Google cannot delete information from a website. Still, once it’s been removed, Google usually removes the listing from its search results within a few days.
Thanks for Reading This Far
We hope this guide to deleting things from the internet has been helpful, and we wish you the very best in attaining your goals.
About the author
Kent Campbell is the chief strategist for Reputation X, an award-winning online reputation management agency. He has over 15 years of experience with SEO, Wikipedia editing, review management, and online reputation strategy. Kent has helped celebrities, leaders, executives, and marketing professionals improve their online appearance. Kent writes about reputation, SEO, Wikipedia, and PR-related topics and is an expert witness for reputation-related legal matters.
–
Tags: Online Reputation Management Services, Online Reputation Repair, Reputation Management.
