What Makes Company Reputation Such a Valuable Intangible Asset?
Business assets are often thought of as tangible things that provide service or value to the company that owns them, such as equipment, cash, raw materials, or real estate. But there are valuable properties in business that are not physical. These include patents, goodwill, and a good corporate reputation.
As long as a company’s reputation is maintained as an asset and is not damaged, it will provide long-term value to the business. While a hard figure can be challenging to assign to an intangible asset such as reputation, the evidence of the high value of corporate reputation is clear and irrefutable.
Article sections
- What is corporate reputation?
- What are tangible vs. intangible assets?
- What are some advantages of having a good corporate reputation?
- What is the value of reputation?
- How do you manage your reputation?
- FAQs
What is corporate reputation?
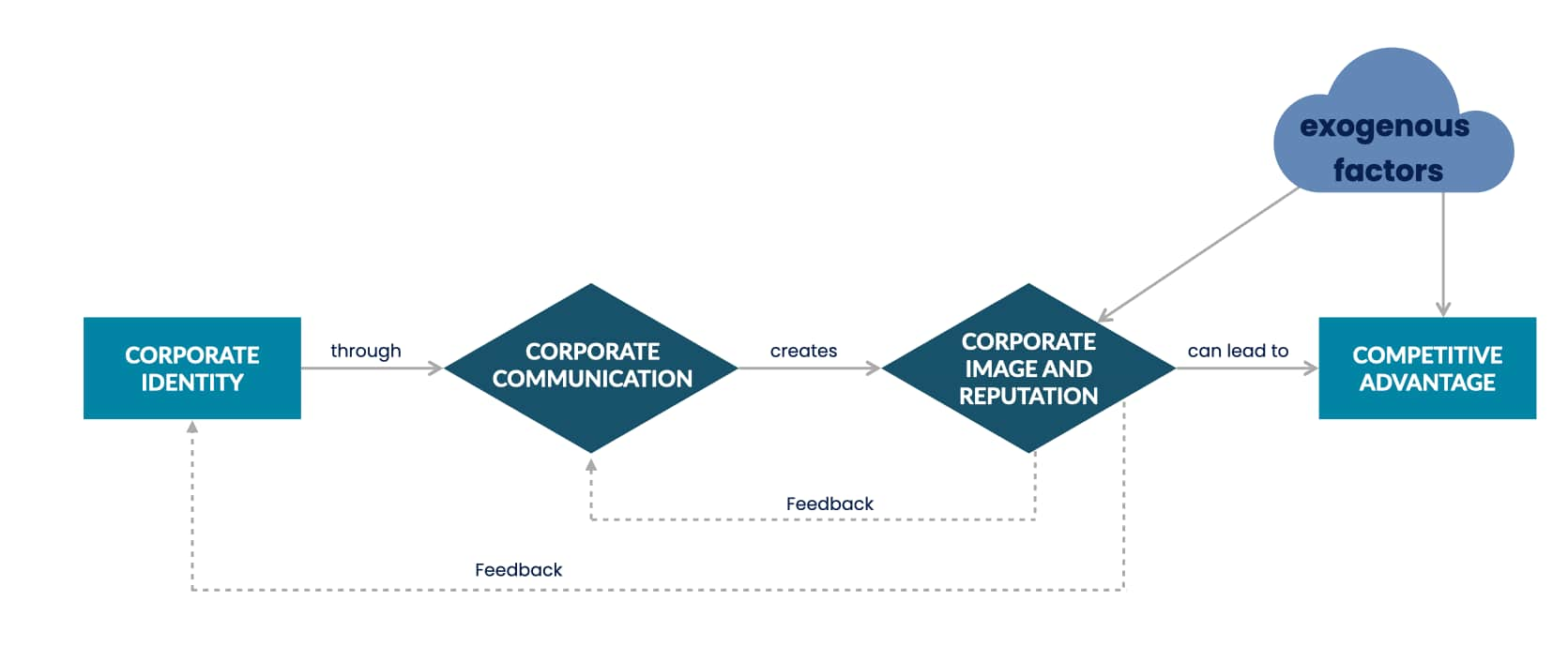
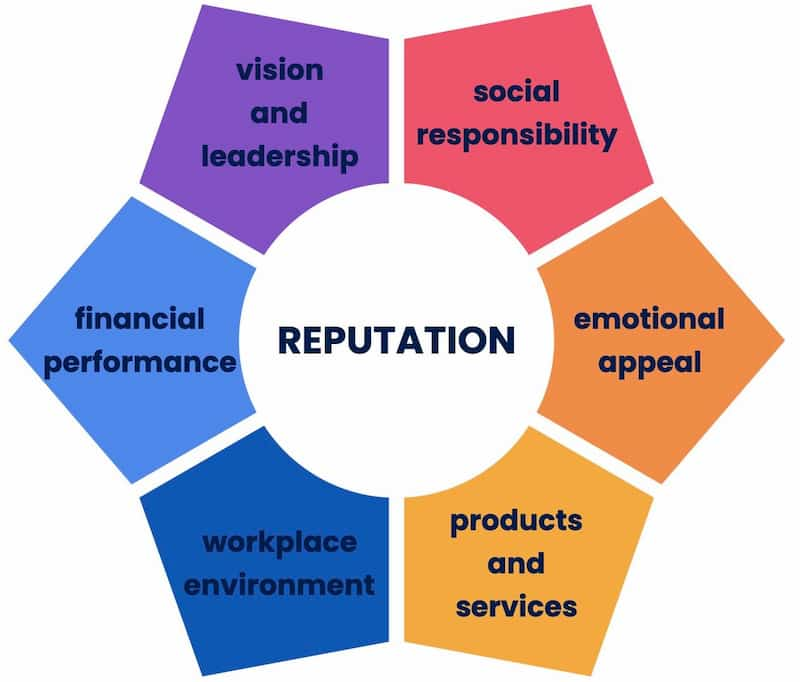
Corporate reputation is the general opinion held by primary and secondary stakeholders about a company’s past, its current status, and the predictability of its future. It’s conceived through the perceptions and expectations of the public and based heavily on brand story and emotional appeal, financial and leadership performance, and actions both known and perceived. A considerable portion of corporate reputation is generated on Google, social media, and other online sources. Factors that influence reputation include:
- Quality of products and services
- Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Financial performance
- Brand story
- Work environment
- Leadership and vision
- Emotional appeal
- Partners, suppliers, and affiliates
- Employee behavior and competence
- Regulatory adherence
- Online reputation
What are tangible vs. intangible assets?
Tangible assets are physical assets such as property, buildings, equipment, raw materials, and inventory, etc. A company’s cash reserves are tangible assets, too, as are their employees.
An intangible asset is something valuable that a company owns that is not physical in nature. Intangible assets include things like patents, copyrights, and trademarks, as well as brand recognition and reputation. Both tangible and intangible assets offer considerable value to the company that owns them.
What are some advantages of having a good corporate reputation?
A positive corporate reputation improves both short-term and long-term financial performance. Because a good reputation is not something that is quickly and easily acquired, it provides a sharp competitive edge.
Advantages of having a good corporate reputation may include:
- Better access to capital and investors
- Better share performance
- Larger customer base
- Better pricing options
- Higher average lifetime customer value
- Increased revenue
- More applicants per role
- Higher-quality talent pool
- Increased retention
- Less scrutiny from government and regulators
- Preferential access to projects
- Policy influence
- Positive media coverage
- Broader networking
- Influence on industry research
- Access to new sectors
- Better public rapport
- Free publicity
- Links with community leaders
- Community support for business expansion
What is the value of reputation?
In less than 30 years, the average company has gone from having 95% of its value based on tangible assets to having 75% of its value based on its corporate reputation, a very intangible asset.
A good reputation has a ripple effect that improves the value of your business and ultimately reproduces itself. It helps your company attract top talent, positively impacts the productivity of your employees, and increases the willingness and determination of partners, suppliers, creditors, and regulators to work with you. This in turn lowers your production costs and costs of capital and improves your margins and pricing options, which will improve your company’s financial analyses and drive demand for your shares.
A positive reputation can even have a more direct impact on your bottom line, as it also increases your average lifetime customer value and market share. This increase in value is known as brand reputation value. A strong brand reputation value brings a company greater profit. Three out of five CEOs believe their reputation represents over 40% of their companies’ market capitalization.
How do you manage your reputation?
Your company reputation should be managed carefully, like any other valuable asset. For tangible assets, a company allocates resources to things like product development, operation, maintenance, and sales. The intangible asset of your company’s reputation is every bit as valuable – if not more so. Properly investing in your corporate reputation requires allocating resources to areas like leadership, quality control, product and service, workforce care, risk management, and social responsibility. Your secondary stakeholders, such as the general public, community, and media, are immensely important to your reputation, so consider them while developing your strategies.
Corporate reputation management and improvement tactics
- Identify areas with room for improvement that are potentially the most profitable and invest in at least three of them.
- Invest for long-term returns. Reputation value isn’t a short play, but rather a long game of building the value of your company by developing a strong competitive edge and a reservoir of goodwill.
- Insure against both direct and indirect reputational damage by developing strong screening practices for both employees and partners and maintaining adherence to your corporate values.
- Encourage open communication with compliance officers and every level of your corporate structure.
- One of the most effective ways to improve your reputation is by designing an emotional appeal to consumers. You can achieve this by building a strong brand story and – importantly – investing your company in community programs, environmental impact improvements, and other corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
Corporate reputation as an intangible asset FAQs
What is meant by intangible assets?
Intangible corporate assets are assets that are owned by and bring value to the company but cannot be physically touched. Good examples of intangible assets are corporate reputation, brand recognition, goodwill, patents, and copyrights (as opposed to physical, tangible assets like land, facilities, equipment, and vehicles). Corporate reputation is the most valuable intangible asset because it generates such massive value for a company and its bottom line.
What are the major types of intangible assets?
The term “intangible assets” typically refers to a company’s reputation, patents, copyrights, trademarks, and brand. These are things owned by a company that add value but cannot be touched. Corporate reputation is a relatively new field of study but falls in the category of major intangible assets when considering company value and strategies for asset management.
What are the two main characteristics of intangible assets?
Intangible assets do not have a physical presence and cannot be financial instruments. Intangible assets are typically classified as long-term assets because they provide value for at least several years. In the case of a corporate reputation, the intangible asset will provide value for the life of the company, assuming the reputation is not damaged or destroyed.
Tags: Business Reputation Marketing, Corporate Reputation, Reputation Management.