Why Is The News So Negative? Negativity Biases, Media Bias, and More.
Imagine that you saw two news articles. The first headline said “The weather is beautiful today!” while the second proclaimed that a dark storm was headed your way. Which would you click on?

Most likely the second one, because you want to know how the storm may affect your day. Have you ever noticed why there is so much negativity in the news? Leveraging negative content has been used by the media for years, urging viewers to stay tuned to hear how certain things might be dangerous or cause turmoil in their life. Negativity draws eyeballs, which in turn will result in the negative news ranking higher than the positive news.
Table of Contents:
- The Prevalence of Negative News
- Understanding Negativity Bias
- Impact of Negative News on Consumers
- The Role of Media in Amplifying Negativity
- Ways to Address Negativity in News Consumption
The Prevalence of Negative News
Studies reveal that more than half of all news stories contain a significantly higher number of negative assertions compared to positive ones. This trend is not isolated to any specific medium. In fact, it spans across digital platforms, print, and broadcast. Internet sources like National Review Online, Slate, and Salon show even higher negativity rates. For instance, approximately 63% of stories on these platforms are negatively toned compared to 53% in newspapers.
This prevalence of negative news is further amplified by the inherent human attraction to negative information. This is a phenomenon known as the “negativity bias.” Our cognitive wiring predisposes us to pay more attention to negative news, which historically might have helped in recognizing and avoiding dangers. This bias is evident across various demographics and is not confined by age, gender, or political ideology.
Moreover, the phrase “if it bleeds, it leads” encapsulates the media’s long-standing intuition that stories involving crime, tragedy, or scandal are more likely to attract viewers and readers. This focus on negative content is not just a reflection of media preference but also a response to consumer demand. As such, negative headlines, which often contain words like “bad,” “worst,” or “never,” are shown to increase engagement significantly. They also catch 30% more attention and yield higher click-through rates. This often applies to negative reviews as well, which tend to be difficult for business owners to remove.
Reputation X highlights that understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing strategies to manage and counteract the overwhelming presence of negative news, advocating for a balanced approach in news consumption and reporting.
Understanding Negativity Bias
Negativity bias, an inherent human inclination, intensifies our reactions to negative stimuli compared to positive ones. This bias is not merely a psychological curiosity but a deeply ingrained evolutionary trait that has helped humans survive by quickly identifying and reacting to potential threats.
Studies reveal that negative events provoke a stronger and quicker emotional response than positive or neutral events, highlighting the critical survival functions this bias served in our evolutionary past. Understanding how negativity bias affects one’s reputation can be a powerful tool when managing reputation online.
Origins and Evolution
Historically, negativity bias allowed our ancestors to stay alert to environmental dangers, thus ensuring their survival. This predisposition to prioritize negative information over positive is evident not just in humans but across various species, suggesting a fundamental evolutionary advantage.
Psychological Studies
Research indicates that this bias influences various psychological domains, from early development in infants to complex decision-making in adults. For instance, infants show a preference for negative information, which plays a crucial role in their cognitive and emotional development. Adults, similarly, are more attuned to negative news, which often results in a greater impact on their psychological state and decision-making processes.
Negativity Bias in Media
When it comes to the news and media, negativity bias explains why bad news often dominates. This predilection isn’t just a media creation but a reflection of what captivates human attention. Media outlets, driven by the need to attract viewers or readers, often emphasize negative stories, which can exacerbate the perception of negativity bias in news consumption.
By understanding these mechanisms, we can better navigate our responses and perhaps mitigate some of the bias’s less desirable effects on our personal and societal well-being.
Impact of Negative News on Consumers
Negative news impacts consumers profoundly, influencing both their emotional state and behaviors. The constant exposure to distressing content can lead to distrust towards media outlets. Studies show that sensational stories and perceived media bias foster skepticism among viewers. This skepticism is compounded by the prevalence of fake news, further eroding trust.
Emotional and Physical Effects
The barrage of negative news triggers stress responses that are not just psychological but also physical. Symptoms such as increased anxiety, fear, and a general sense of unease can manifest. This continuous stress response can have long-term health implications, including chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
Behavioral Changes
Exposure to negative news can alter consumer behavior significantly. People may become more cynical, less likely to engage with news, or shift their media consumption habits entirely. The presence of negative headlines increases the likelihood of clicking on a news story. This indicates that even as consumers may express distrust, the engagement with content persists, driven by a deep-seated negativity bias.
In this graph for example, some countries have nearly half of their populations avoiding the news.
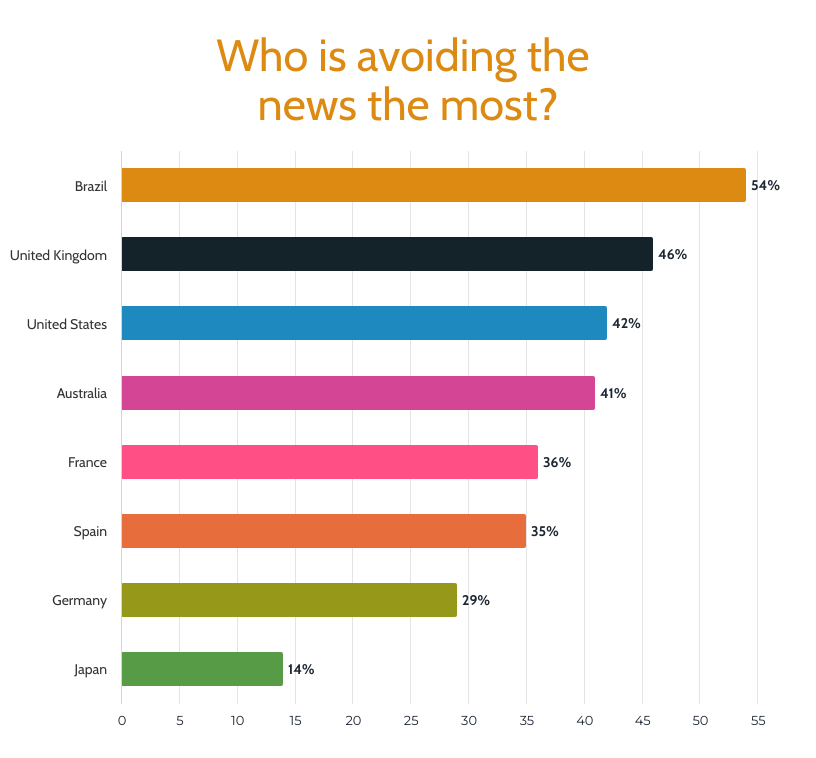
Trust in Media
The credibility of news organizations suffers when consumers are repeatedly exposed to negative and sensational content. This distrust is exacerbated by the spread of misinformation and fake news, which directly challenges the integrity of established news sources. As trust declines, the challenge for the media becomes not just about reporting the news but also about proving its veracity and impartiality to an increasingly skeptical public.
The Role of Media in Amplifying Negativity
Social media algorithms significantly contribute to the amplification of negativity in news content by prioritizing user engagement over the accuracy of information.
This approach often results in the promotion of content that triggers emotional reactions. They are: prestigious, ingroup, moral, and emotional (PRIME) information, which may not accurately represent a group’s overall opinions. The tendency to highlight extreme political content or controversial topics can mislead users, giving a skewed perception of majority viewpoints.
Clickbait and Sensationalism
Clickbait techniques further exacerbate this issue by using sensational headlines to attract clicks, often at the expense of truth and depth in reporting. This strategy not only misinforms but also contributes to a cycle of misinformation and superficial reading, where users do not engage deeply with the content.
Economic Incentives
The drive for higher engagement is closely tied to economic incentives, as media outlets rely on advertising revenue. This dependency compels platforms to engage users at any cost, prioritizing sensational content that is more likely to be shared and discussed, regardless of its factual accuracy.
Social Media Algorithms
Efforts to mitigate the negative effects of these algorithms include educating users about how their feeds are curated and adjusting algorithms to limit the spread of PRIME information. By promoting a more diverse array of content, social media platforms can help foster community and reduce polarization.
However, these changes require a concerted effort from both tech companies and users to prioritize accuracy and community over mere engagement. Paying attention to social media trends is also a good way to measure corporate reputation.
In the chart below, you can see how 64% of adults in the United States view the effects social media has had a mostly negative effect on the country.
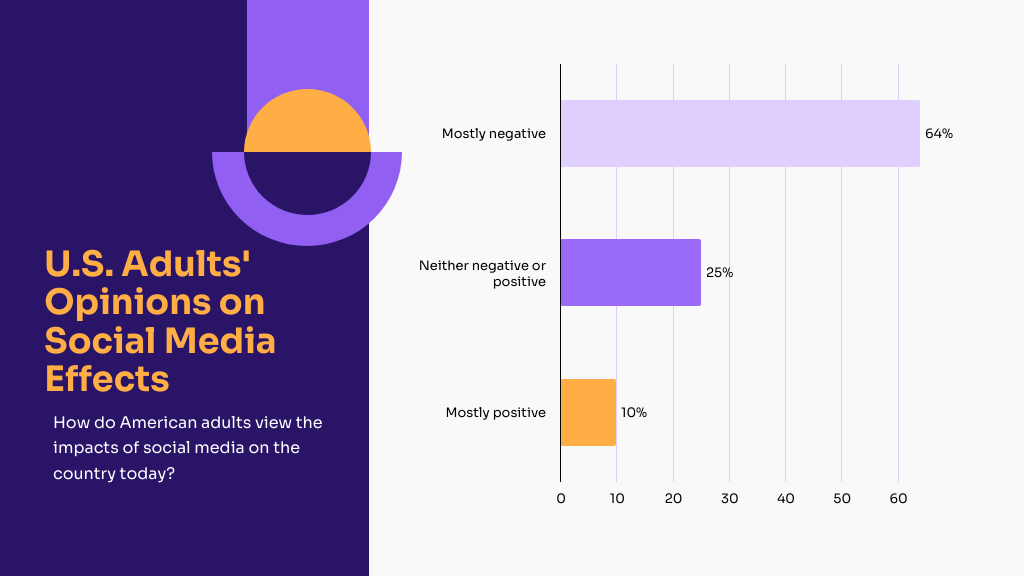
Ways to Address Negativity in News Consumption
Seeking Balanced News Sources
To counteract the prevalence of negative news, consumers are encouraged to seek out balanced news sources known for journalistic integrity, such as Reuters and The Associated Press. These organizations strive for balanced reporting and are less influenced by political bias. Engaging with a variety of news sources, including those with differing perspectives, helps individuals develop a more nuanced understanding of issues, reducing the impact of negativity bias.
Practicing Media Literacy
Consumers should learn to access, analyze, and evaluate the media they consume. This includes understanding the biases that may influence news stories and recognizing clickbait that skews facts. Moreover, Media literacy empowers individuals to make informed decisions about the credibility of information, thereby mitigating the effects of negative news.
Promoting Positive News Initiatives
Supporting platforms that focus on positive news, such as Positive News and Sparknews, can alter the impact of negativity in media. These organizations highlight constructive journalism and solutions-based stories, which can provide a more balanced media diet. By promoting news that focuses on solutions and positive developments, consumers can foster a more optimistic view and reduce the psychological burden of negative news.
FAQs
- Why does the news predominantly feature negative stories?
- The tendency for news to appear negative can largely be attributed to human nature. Physiologically, people react more intensely to negative news, as indicated by increased skin conductance levels and heart rate variability. This heightened attention to negative stimuli is a natural human response.
- What does “bad news bias” mean in the context of media?
- The term “bad news bias” refers to the phenomenon where negative information captures more attention than positive information. Social psychologists identify this as a “negativity bias,” where individuals show a preference for negative over positive news. This bias significantly influences the overall tone of media coverage, making it seem more depressing.
- Why do news outlets tend to publish more negative stories?
- The prevalence of negative stories in news media can be linked to a psychological bias where humans are more attuned to negative stimuli, such as recognizing angry faces more readily than happy ones. Many languages also have more terms to describe negative emotions compared to positive ones. This focus on the negative is thought to stem from an evolutionary survival mechanism that influences our preferences in news.
- What makes people more drawn to negative news compared to positive news?
- People are generally more attracted to negative news due to the “negativity bias,” where the brain prioritizes potential threats. This bias ensures that negative or threatening information elicits stronger and more immediate emotional responses compared to positive news. This instinctual reaction plays a significant role in the type of news that garners more attention and emotional engagement.
About the author
Kent Campbell is the chief strategist for Reputation X, an award-winning online reputation management agency. He has over 15 years of experience with SEO, Wikipedia editing, review management, and online reputation strategy. Kent has helped celebrities, leaders, executives, and marketing professionals improve the way they are seen online. Kent writes about reputation, SEO, Wikipedia, and PR-related topics, and is an expert witness for reputation-related legal matters.
–
Tags: Business Reputation Repair, Online Reputation Management Services, Reputation Management, Reputation Marketing.
