How to Search Online Without Being Caught
Even though the internet is a valuable source of information, it presents multiple security risks and vulnerabilities, such as cybercrime, which are rapidly increasing due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Therefore, individuals should implement safe browsing habits and reduce their digital footprints as much as possible.
But first, let’s learn more about the digital footprint and how to reduce it when browsing online.
What Is a Digital Footprint?
A digital footprint is the trail of information and data you leave while browsing the internet. Naturally, the more time you spend online, the larger the digital footprint you leave behind.
Generally, there are two types of digital footprints:
- Active – the personal information purposely shared by the user through social media platforms and websites. This could be a blog post, social media updates, and comments.
- Passive – the information shared without the user knowing. This includes your browser search history, IP address, website cookies, and internet service provider information.
Why Reduce Your Digital Footprint?
Companies usually collect your information from your digital footprint for marketing purposes, such as understanding your shopping preferences and seeing your location.
While most of it is harmless, reducing your digital footprint is still an effective security measure. Some of the benefits of reducing digital footprints are:
- Reducing attempts of cyberbullying and identity theft.
- Blocking unwanted ads.
- Protecting your data and privacy, which is especially important if you’re running a business.
However, leaving digital footprints isn’t always a bad thing. When managed correctly, leaving digital footprints can help your personal and professional development, for example, seeing job openings as ads when searching for a job.
9 Tips to Reduce Your Digital Footprint
These nine tips combine knowledge on how to browse safely and take security measures for your device.
Let’s recap the nine tips to reduce your digital footprints:
- Use hidden browsing mode
- Use a VPN
- Clear browsing data
- Deactivate old accounts
- Be careful with public wi-fi
- Avoid storing passwords on your browser
- Block unnecessary cookies
- Clean up regularly
- Block pop-ups
1. Clear Browsing Data
This means deleting data such as your name, phone number, and email address you input when browsing, including cookies and cache.
Website cookies remember the sites you go to, and cache remembers files and images in those websites. While they help enhance user experience, it’s a risk not to clear cookies and cache.
When you clear cookies and cache, you’re deleting your tracks. Therefore, making it more difficult for websites and attackers to track you. Clearing browsing data is also an excellent solution to fix SSL connection errors.
To clear browsing data on Google Chrome browser, open History > History > click Clear browsing data on the left tab.
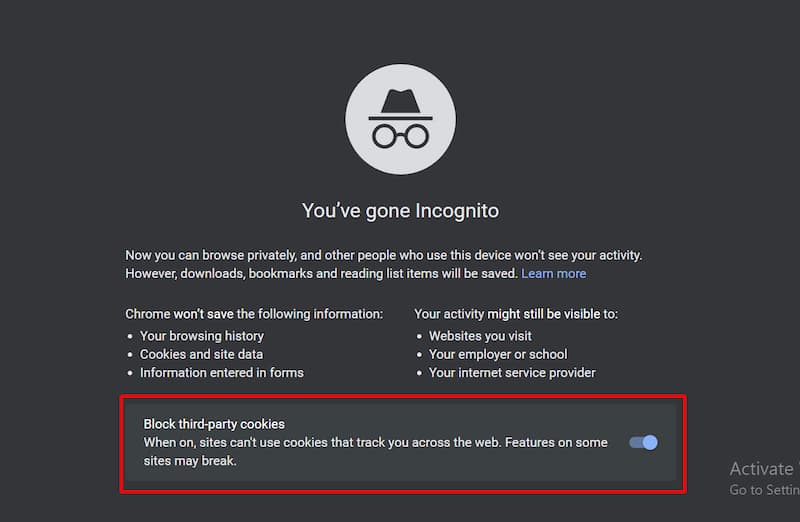
2. Use Hidden Browsing Mode
Private browsing refers to hiding your browsing. Use the Incognito mode on Chrome and Private mode on Firefox to do so.
Using a hidden browsing mode is safer because you leave less of a digital footprint, making your personal information safe and preventing websites from tracking you. Private browsing mode also blocks third-party cookies.
It’s especially important to use private browsing whenever you use a public computer or shop online.
To activate the hidden browsing mode on MacOS, use the shortcut Command-Shift-P. If you’re using Windows, use Ctrl-Shift-N to go to incognito mode.
3. Use a VPN
Virtual Private Network (VPN) is an extra layer of security that protects your privacy and information when you’re on the internet.
Using a VPN makes your IP address invisible to everyone, ensuring your data privacy.
Choose a VPN service of your choice for your desktop and mobile devices, and use it whenever you need extra privacy. Some of the popular options are NordVPN, ExpressVPN, and Surfshark.
If you’re running a business, consider paid VPN plans for better security and privacy.
4. Deactivate Old Accounts
Your email, social media, and other digital accounts contain personal information. While sharing personal information can be helpful, it can also harm you.
Therefore, always deactivate your old accounts when you no longer need them, even if you’ve deleted the app from your computer or smartphone.
Start listing all your old accounts and delete or deactivate them. Furthermore, when you’re creating a new account, give as little personal information as possible.
5. Be Careful With Public Wi-Fi
Whenever you’re in a public space, always be careful with public wi-fi, especially with the one without any password. Using public wi-fi is risky because it makes you more vulnerable to hacking and potential attackers trying to steal your information.
Always avoid using public wi-fi and use your mobile internet data instead. But if it’s not an option, here are some safety measures to take:
- Ensure the wireless connection is legitimate.
- Be aware of suspicious links.
- Stick to HTTPS websites.
- Avoid inputting sensitive personal information, like bank account details, personal identification numbers, and an insurance number.
- Protect your device with antivirus or firewall software.
6. Avoid Storing Passwords on Your Browser
Storing your passwords on your browser is effective because you don’t need to type passwords when logging in to accounts. Also, browsers like Google Chrome always offer to save passwords.
However, avoid storing passwords on your browser unless you’re certain that nobody else has access to your computer or smartphone.
If your device is lost or stolen, people can easily log in to your account because the password is stored on the browser. Also, hackers can access your computer and see all your passwords.
For safety measures, never choose the “Save password” option when logging in to websites. Prevent attacks by creating strong passwords and changing them regularly.
Alternatively, use a password manager instead, like LastPass or 1Password.
7. Block Unnecessary Cookies
Website cookies can be helpful as they create files that save user preferences and help improve the browsing experience. The best practice for website cookies is to keep the important ones and block the unnecessary ones.
To identify the unnecessary cookies, use your antivirus software as it’s able to detect flagged or suspicious cookies. Also, manage your cookies whenever you visit a new website.
8. Clean Up Regularly
Another measure to reduce digital footprints is cleaning up your data, software, and browser regularly. Doing so ensures you don’t store unnecessary data/files and not leave trails for unwanted parties.
It also helps to audit your existing digital footprints and go from there. Unsubscribe from services you no longer need and adjust your privacy settings on different browsers and accounts.
Set a schedule to ensure that you clean up regularly.
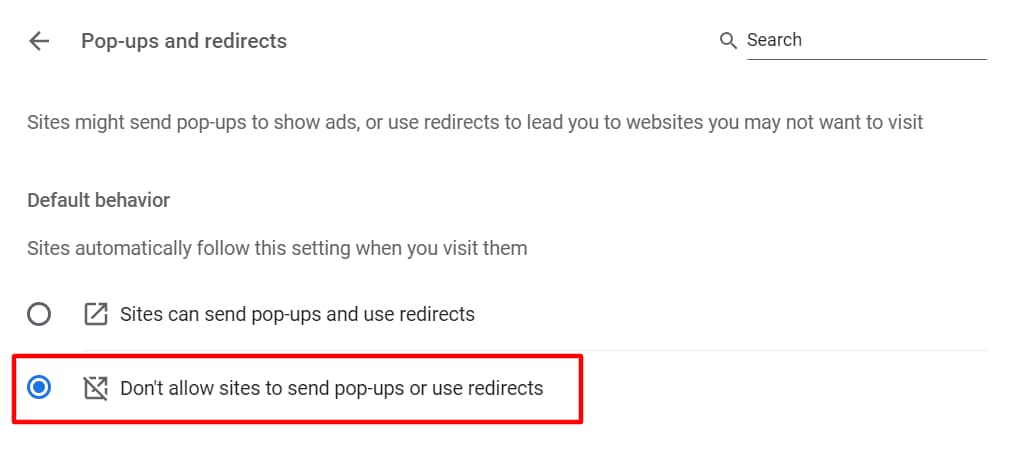
9. Block Pop-Ups
Most pop-ups are ads, malware, and other unwanted windows that clutter your browsing experience. By blocking pop-ups, you reduce phishing and scam attempts.
Blocking pop-ups is as simple as activating the pop-up blocker on your computer and smartphone.
To block pop-ups on Google Chrome, go to Settings > Site settings > Choose “Don’t allow sites to send pop-ups or use redirects”
Final Thoughts
Digital footprints are the information you leave behind when browsing online. There are two types of digital footprints – active and passive.
Reducing digital footprints is beneficial to protect your data, privacy, and reputation. It also helps prevent cyberattacks from happening.
Let’s recap the nine tips to reduce your digital footprints:
- Use hidden browsing mode
- Use a VPN
- Clear browsing data
- Deactivate old accounts
- Be careful with public wi-fi
- Avoid storing passwords on your browser
- Block unnecessary cookies
- Clean up regularly
- Block pop-ups
Keep these safety measures in mind the next time you’re online and protect yourself from any digital security risks.
How to Search Online Without Being Caught FAQs
What is a digital footprint?
A digital footprint is the trail of information and data you leave while browsing the internet. Naturally, the more time you spend online, the larger the digital footprint you leave behind.
What are the different types of digital footprints?
There are two main types of digital footprints. Active digital footprints contain the personal information purposely shared by the user through social media platforms and websites. This could be a blog post, social media updates, and comments. Passive digital footprints contain the information shared without the user knowing. This includes your browser search history, IP address, website cookies, and internet service provider information.
How can I reduce my digital footprint?
The following tips can help you reduce your digital footprint. Use hidden browsing mode. Use VPN. Clear browsing data. Deactivate old accounts. Be careful with public wi-fi. Avoid storing passwords on your browser. Block unnecessary cookies. Clean up regularly. Block pop-ups.
Tags: Reputation Protection.